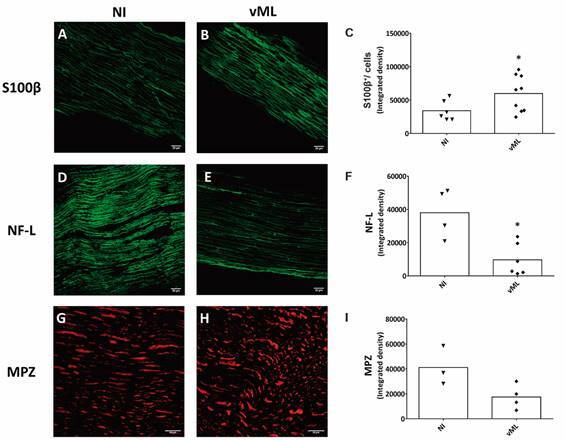
Fig. 2: immunophenotypic characterisation of mouse sciatic nerves. Sciatic nerves were resected from healthy nude mice non-infected (NI) or mice inoculated with viable Mycobacterium leprae (vML) during eight months. Nerves were cryopreserved and incubated with the following primary antibodies and corresponding secondary antibodies: S100β (green, AlexaFluor 488, Molecular Probes); NF-L (green, AlexaFluor 488, Molecular Probes), and MPZ (red, AlexaFluor 594, Molecular Probes). Confocal images illustrate fluorescent detection of S100β (A-B), NF-L (D-E) and MPZ (G-H). Scale bar = 20 µm. (C, F, I) Graphs showing scatter plots with mean values, obtained from unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction. *p < 0.05. Each dot in scatter plots represents nerve fragments, one per animal. Immunofluorescence was performed in 3-6, and 4-9 nerve fragments in NI and vML-infected mice, respectively.