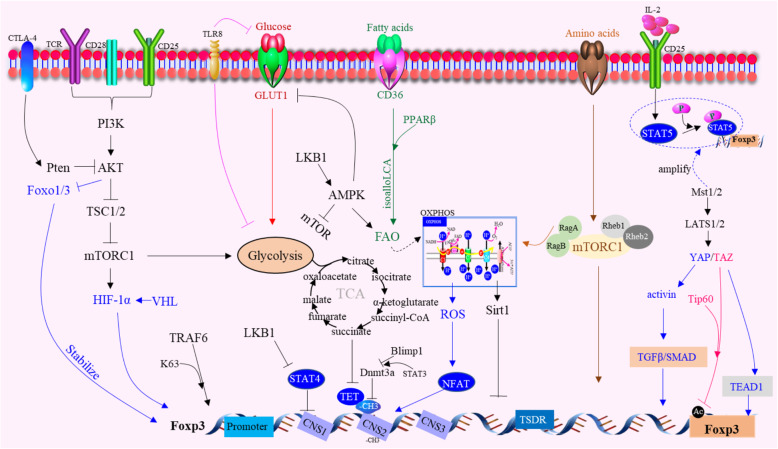
Fig. 4.
Metabolic regulation of Foxp3 expression. Environmental metabolites, intracellular metabolic intermediates and signaling pathways all regulate Foxp3 expression in Tregs. LKB1 prevents STAT4 activation and binding to CNS2 of Foxp3 gene, thus preventing the destabilization effect. E3 ubiquitin ligase VHL can regulate HIF-1α to maintain the stability and suppressive capacity of Tregs. Foxp3 opposed PI3K-Akt-mTORC1 signaling to decrease glycolysis and anabolic metabolism while increasing oxidative and catabolic metabolism. CD36 finetuned mitochondrial fitness via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-beta (PPARβ) signaling, programming Tregs to adapt to a lactic acidenriched TME. The deletion of TRAF6 in Tregs were resistant to implanted tumors and displayed enhanced antitumor immunity due to that Foxp3 undergoes K63-linked ubiquitination at lysine 262 mediated by the E3 ligase TRAF6. The specific ablation of RagA-RagB or Rheb1Rheb2 in Tregs has reduced Tregs accumulation and function. RagA-RagB regulated mitochondrial and lysosomal fitness, while Rheb1Rheb2 enforced Tregs suppressive gene signature licensed by amino acids. YAP-dependent upregulate activin signaling, which amplifies TGFβ/SMAD activation in Tregs. TAZ attenuated Tregs development by decreasing acetylation of Foxp3 mediated by the histone acetyltransferase Tip60. TEAD1 expression and sequestration of TAZ from the transcription factors Foxp3 promotes Tregs differentiation. TLR8 signaling selectively inhibits glucose uptake and glycolysis in human Tregs, resulting in reversal of Tregs suppression. Mst1promote Tregs migration and access to IL-2 and activity of the small GTPase Rac, which mediated downstream STAT5 activation. Mst1-Mst2 sensed IL-2 signals to promote the STAT5 activation necessary for Tregs homeostasis and lineage stability and to maintain the highly suppressive pSTAT5+Tregs