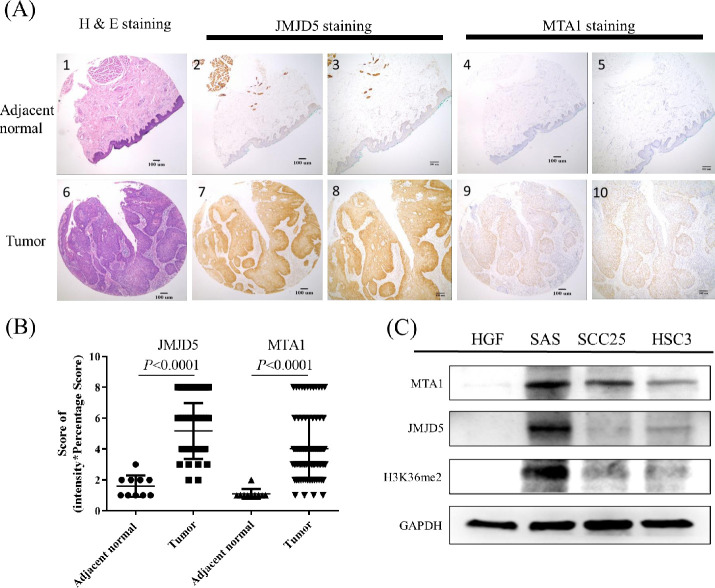
Fig 1. JMJD5 and MTA1 were overexpressed in oral cancer.
Representative samples scored for high or low expression for JMJD5 and MTA1 IHC results are shown. (A1) H&E stain for normal tissues adjacent to the tumor (magnification 40x); (A2) JMJD5-stained in normal tissues adjacent to the tumor (magnification 40x); (A3) JMJD5-stained in normal tissues adjacent to the tumor (magnification 100x); (A4) MTA1-stained in normal tissues adjacent to the tumor (magnification 40x); (A5) MTA1-stained in normal tissues adjacent to the tumor (magnification 100x); (A6) H&E stain for OSCC tumor tissue (magnification 40x); (A7) JMJD5-stained in OSCC tumor tissue (magnification 40x); (A8) JMJD5-stained in OSCC tumor tissue (magnification 100x); (A9) MTA1-stained in OSCC tumor tissue (magnification 40x); (A10) MTA1-stained in OSCC tumor tissue (magnification 100x). (B) JMJD5 and MTA1 were highly expressed in oral cancer tissues. The score was defined intensity score x percentage score. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test) is represented significance difference. (C) Both JMJD5 and MTA1 were high expressed in the oral cancer cell lines than in normal cells. HGF as a primary cultured normal human gingival fibroblast cell. H3K36me2, the di-methylation at the 36th lysine residue of the histone H3 protein.