Figure 2. Wnt Proteins in T cells and Dendritic Cells (DCs) in Mice and Humans.
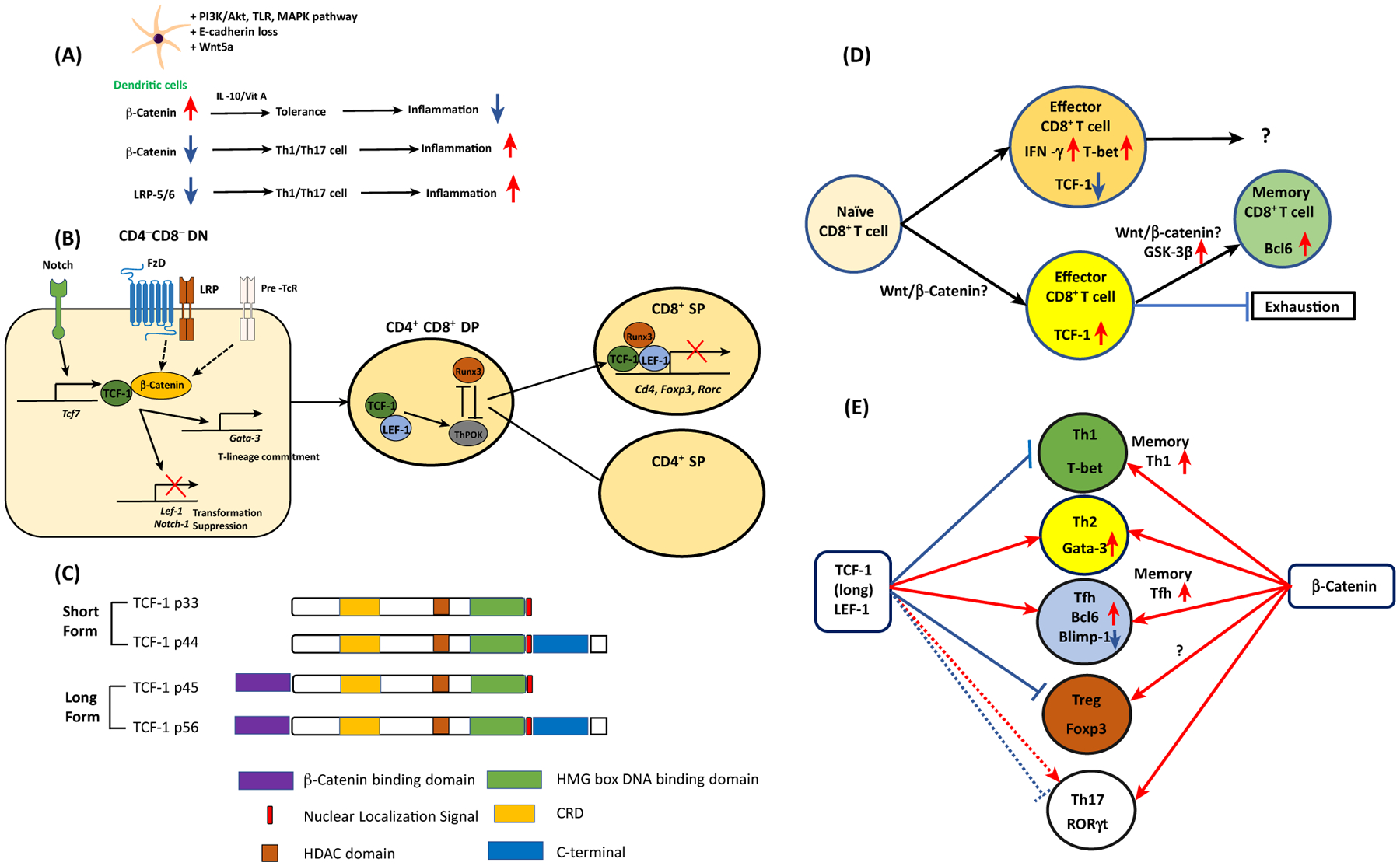
(A) β-Catenin accumulation by various signaling pathways and Wnt5a induces tolerogenic DCs to suppress inflammation. When DCs lack β-catenin or Wnt coreceptors LRP5/6, CD4+ T cells are preferentially differentiated into type 1/17 T helper (Th1/Th17) cells to promote inflammation. (B) In the CD4CD8 DN stage, thymocytes receive Notch signals and induce TCF-1. Together with β-catenin, TCF-1 inhibits thymocyte transformation while directing T-lineage commitment via Gata-3 expression. In the CD4CD8 DP stage, TCF-1 interacts with RUNX3 and ThPOK. The interaction between TCF-1/LEF-1 and RUNX3 directs the development of CD8+ T cells. This transcriptional factor complex represses Cd4, Foxp3, and Rorc gene expression. (C) TCF-1 short and long isoforms and their domains. (D) Naïve CD8 T cells are resistant to become CD8 effector T cells if they are TCF-1hi cells, while TCF-1lo cells become active IFN-γ+ T-bet+ effector T cells. TCF-1hi CD8+ effector T cells become more stem-cell-like memory CD8+T cells with elevated expression of Bcl6. Whether the canonical Wnt pathway is involved in this process is controversial. (E) In CD4+ T cells, naïve CD4+ T cells can be differentiated into five different types of helper T cells according to their lineage-specification transcriptional factors. TCF-1 expression favors Th2 and follicular helper T (Tfh) cell formation while it inhibits Th1 differentiation and Treg suppressor function. The role of TCF-1 in Th17 cells is dependent on the microenvironment. In memory CD4+ T cells, TCF-1 enhances memory Th1 and Tfh cell formation. Unlike TCF-1, expression of β-catenin enhances all types of T cell differentiation and function. Abbreviations: DN, double negative; DP, double positive.
