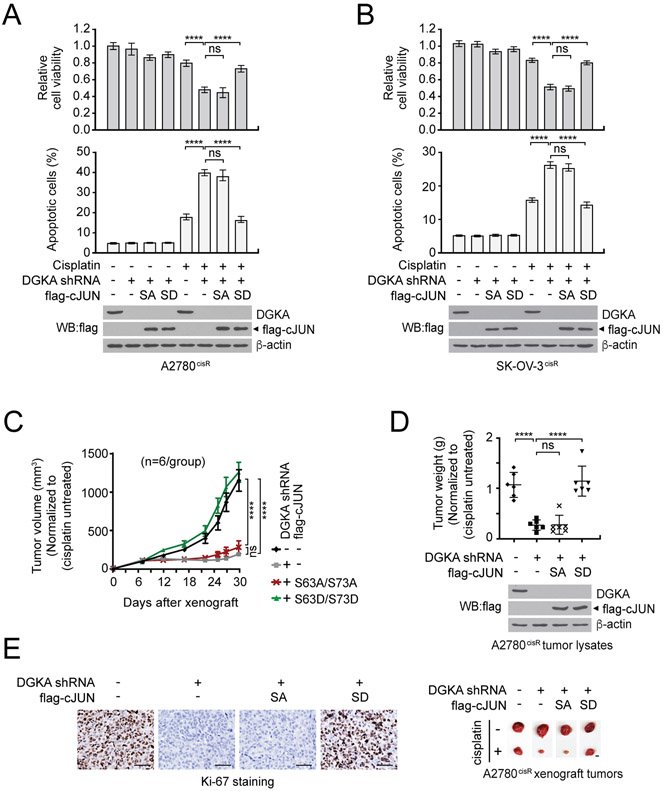
Figure 4. DGKA promotes cisplatin resistance through c-JUN activation.
A and B, Cisplatin-dependent cell viability and apoptotic cell death in A2780cisR (A) and SK-OV-3cisR (B) cells with DGKA knockdown and c-JUN SA (S63A/S73A) or SD (S63D/S73D) expression. Cells were treated with sublethal doses of cisplatin for 48 hr followed by CellTiter-Glo assay and annexin V staining. C-E, DGKA knockdown and c-JUN rescue effect on cisplatin-resistant tumor growth. A2780cisR cells with DGKA knockdown and c-JUN SA or SD expression were xenografted into mice and cisplatin (5 mg/kg/i.p. twice/week) was administered when tumors reached 100 mm3. Tumor volume (C), tumor weight and representative tumor images of each group (D), and Ki-67 staining for tumor proliferation rate (E) are shown. Scale bars represent 50 μm for Ki-67 staining images and 10 mm for tumor images. (A and B) n=3 technical replicates and results of one representative experiment from three independent experiments are shown. (C-E) n=6. Error bars represent SEM for (C) and SD for all rest. P values were determined by two-way ANOVA for (C) and one-way ANOVA for others (ns: not significant; ****P < 0.0001).