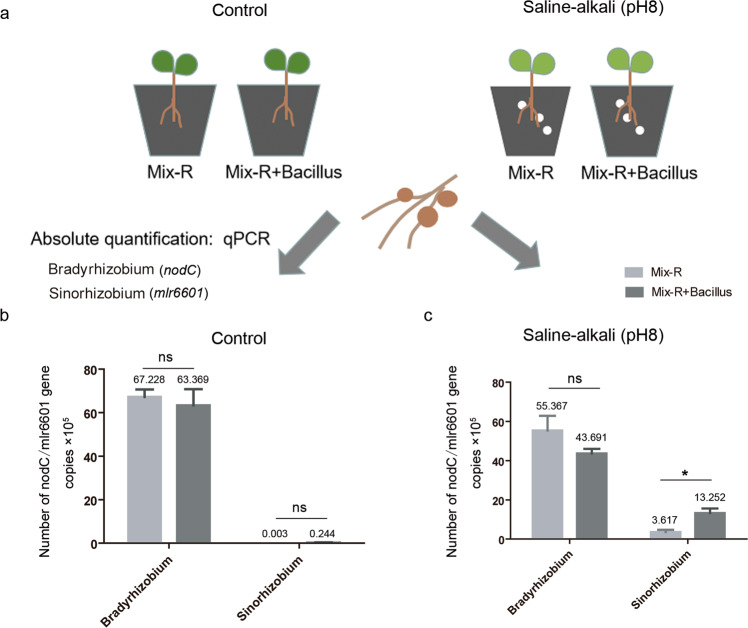
Fig. 6. Effect of Bacillus on the colonization of rhizobia in nodules.
a Schematic representation of the mixed inoculation experiment, showing the planting, inoculation, and quantitative detection methods. Three-day-old plants were transplanted into control or saline–alkali-treated vermiculite, and then plants were inoculated with mixed rhizobia or mixed rhizobia containing Bacillus. Twenty-eight days later, the bacteroid DNA of the nodules was extracted, the concentrations of two kinds of rhizobia were quantified by qPCR, and the experiment was repeated twice. b The populations of Sinorhizobium or Bradyrhizobium bacteroids under control conditions. c The populations of Sinorhizobium or Bradyrhizobium bacteroids under saline–alkali conditions. Mix-R indicates six strains of rhizobium. qPCR results of the Mix-R and Mix-R + Bacillus treatments were analyzed with nonparametric Mann–Whitney tests (n = 4, ns nonsignificant; *P < 0.05). The horizontal bars of each graph indicate the median values and are listed where appropriate for clarity.