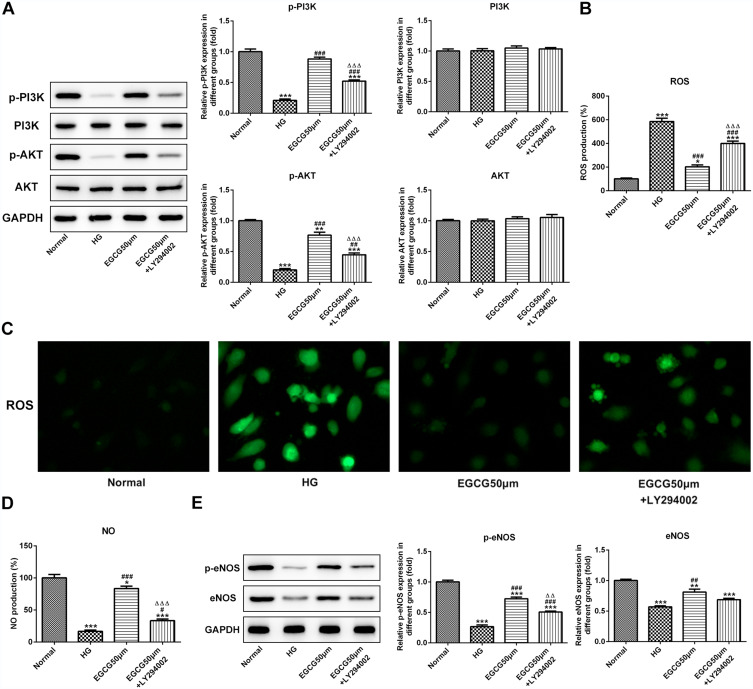
Figure 6.
EGCG alleviates endothelial dysfunction of hyperglycemia-induced vascular endothelial cells by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. (A) The expression of P-PI3K, P-AKT, PI3K and AKT in HG-treated HUVECs affected by EGCG and LY294002 was determined by Western blot analysis. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 vs Normal group. ##P<0.01 and ###P<0.001 vs HG group. ∆∆∆P<0.001 vs EGCG50μM group. (B) The ROS levels in HG-treated HUVECs affected by EGCG and LY294002 was detected by ROS ELISA assay. *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001 vs Normal group. ###P<0.001 vs HG group. ∆∆∆P<0.001 vs EGCG50μM group. (C) The ROS levels in HG-treated HUVECs affected by EGCG and LY294002 was detected by fluorometric ROS assay. (D) The NO levels in HG-treated HUVECs affected by EGCG and LY294002 was analyzed by ROS ELISA assay. *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001 vs Normal group. #P<0.05 and ###P<0.001 vs HG group. ∆∆∆P<0.001 vs EGCG50μM group. (E) The expression of p-eNOS and eNOS in HG-treated HUVECs affected by EGCG and LY294002 was determined by Western blot analysis. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 vs Normal group. ##P<0.01 and ###P<0.001 vs HG group. ∆∆P<0.01 vs EGCG50μM group.