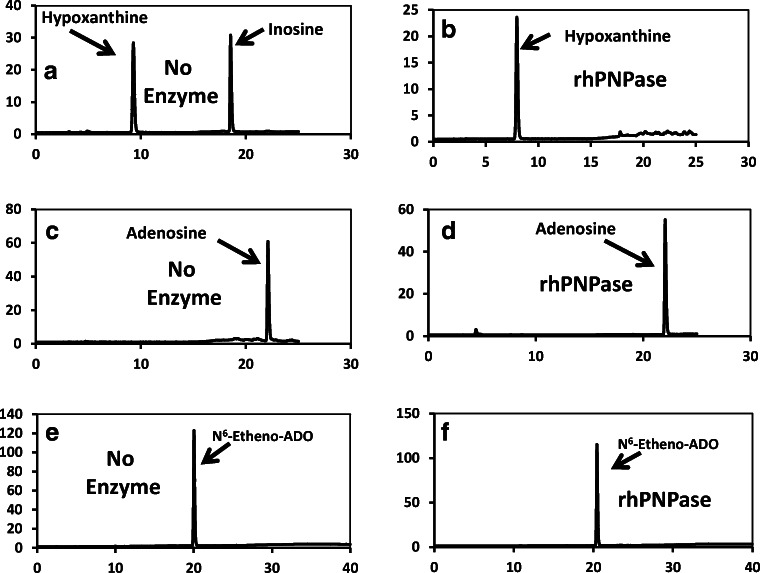
Fig. 10.
a A chromatogram obtained by HPLC-UV of a sample containing both 50 μmol/L of inosine and hypoxanthine incubated (30 min at 30 °C) in the absence of rhPNPase. b A HPLC-UV chromatogram of a sample containing 50 μmol/L of inosine incubated (30 min at 30 °C) with rhPNPase (640 ng). When inosine was incubated with rhPNPase, only a hypoxanthine peak was observed, indicating complete conversion of inosine to hypoxanthine and thus confirming the activity of the rhPNPase. c, d HPLC-UV chromatograms from samples containing 50 μmol/L of adenosine incubated (30 min at 30 °C) without and with, respectively, rhPNPase. As shown, in the presence of rhPNPase, all of the added adenosine was recovered as adenosine. e, f The results of the corresponding experiment with N6-etheno-adenosine (ADO) incubated (30 min at 30 °C) without and with, respectively, rhPNPase. These HPLC-FL chromatograms show that none of the N6-etheno-adenosine was metabolized to N6-etheno-adenine