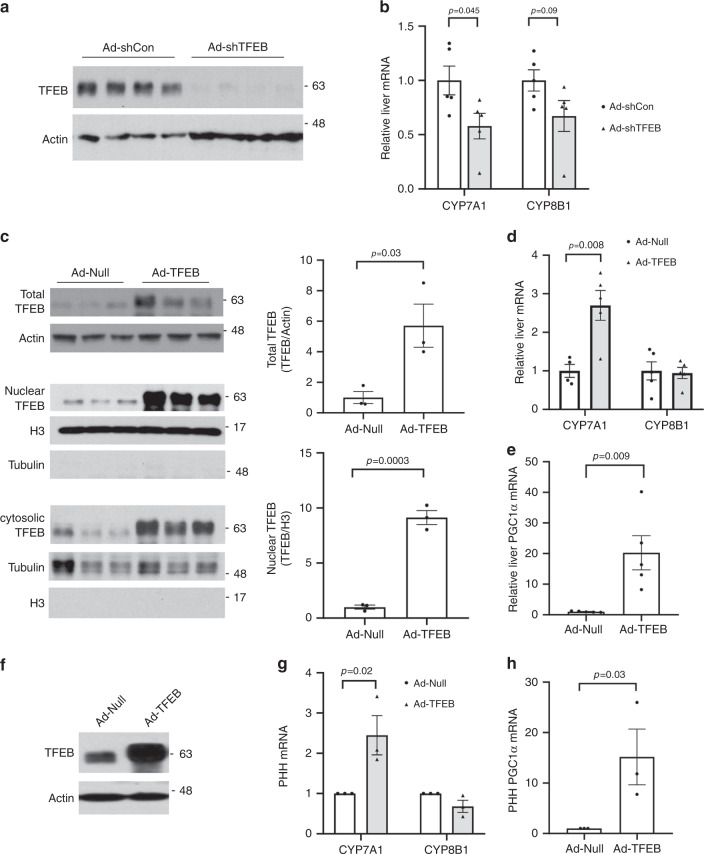
Fig. 1. TFEB induces hepatic CYP7A1 gene expression.
a, b Male 10-week old C57BL/6J mice were injected Ad-Scramble (Ad-shCon) or Ad-shTFEB at a dose of 1 × 109 p.f.u. per mouse via tail vein. Mice were fed chow diet for two additional weeks and sacrificed after 6-h fast. (n = 5 mice per group). a Western blotting of hepatic total TFEB protein. b Hepatic mRNA expression. c–e Male 10-week old C57BL/6J mice were injected Ad-Null or Ad-TFEB at a dose of 5 × 108 p.f.u. per mouse via tail vein. Mice were maintained on chow diet for two weeks and sacrificed after 6-h fast. c Hepatic total, nuclear and cytosolic TFEB protein. H3: histone 3. TFEB band intensity was normalized to Actin or H3. n = 3 mice per group. d Relative hepatic CYP7A1 and CYP8B1 mRNA. (n = 4 mice per group for Ad-Null; n = 5 mice per group for Ad-TFEB). e Relative hepatic PGC1a mRNA expression. n = 5 mice per group. f–h Primary human hepatocytes (PHH) were infected with Ad-Null or Ad-TFEB for 24 h. f A representative blot of total TFEB protein of 3 batches of hepatocytes with similar results. g, h Average mRNA expression of three independent hepatocyte preparations. All results were expressed as mean ± SEM. Two-sided Student’s t-test for b, c, d, and e and one-sided Student’s t-test for g, h was used. Source data for a–h are provided as a Source Data file.