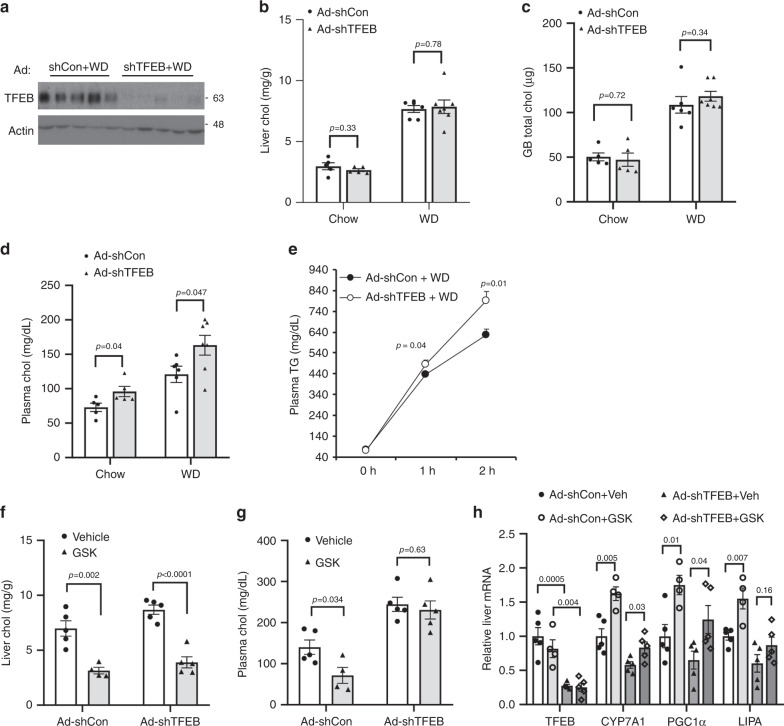
Fig. 9. Hepatic TFEB knockdown exacerbated hypercholesterolemia in WD-challenged mice.
a–d Male 10-week old C57BL/6J mice were injected Ad-scramble (Ad-shCon) or Ad-shTFEB at a dose of 1 × 109 p.f.u. per mouse via tail vein. Mice were fed chow diet for one week and then either fed chow or challenged with WD for one additional week. a. Liver TFEB protein. n = 5 mice per group. b–d Liver, gallbladder (GB) and plasma total cholesterol. n = 5 mice per group for Ad-shCon + Chow; n = 5 mice per group for Ad-shTFEB + Chow; n = 6 mice per group for Ad-shCon+WD; n = 7 mice per group for Ad-shTFEB+WD. e Male 10-week-old C57BL/6J mice were injected Ad-scramble (Ad-shCon) or Ad-shTFEB at a dose of 1 × 109 p.f.u. per mouse via tail vein. Mice were fed chow diet for one week and then challenged with WD for one additional week. VLDL secretion assay was then performed. (n = 5 mice per group). f–h Male 10-week old C57BL/6J mice were injected Ad-scramble (Ad-shCon) or Ad-shTFEB at a dose of 1 × 109 p.f.u. per mouse via tail vein. Mice were either fed chow or challenged with WD for two additional weeks with/without GSK672 (2 mg kg−1 day−1) treatment. Liver total cholesterol (f), plasma total cholesterol (g), and liver mRNA (h) were measured. n = 5 mice per group for Ad-shCon+Veh, Ad-shTFEB+Veh, and Ad-shTFEB+GSK; n = 4 mice per group for Ad-shCon + GSK. All results were expressed as mean ± SEM. Two-sided Student’s t-test was used for b–h. Source data for a–h are provided as a Source Data file.