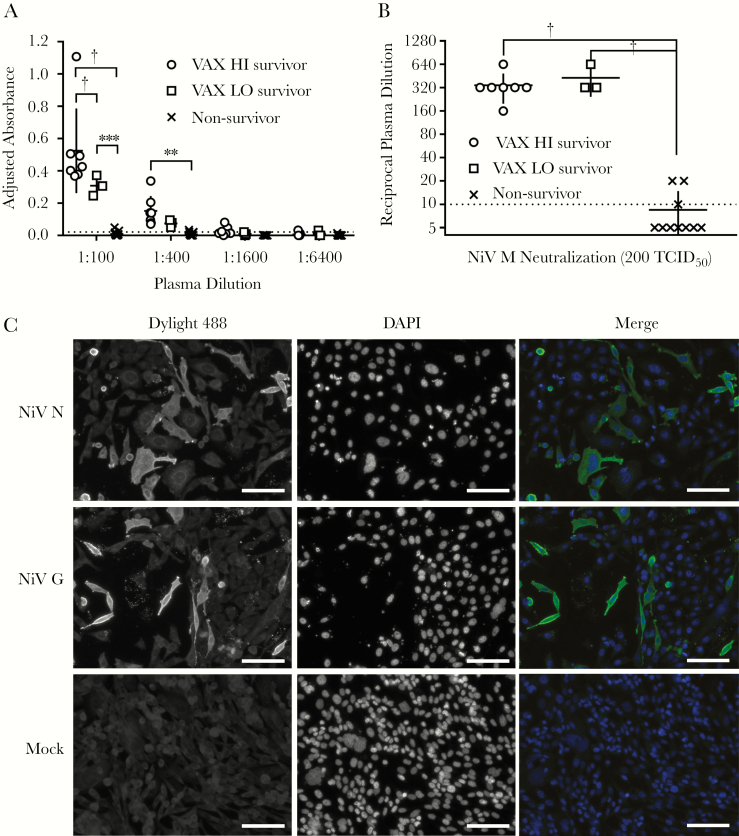
Figure 2.
Survivors among recipients of soluble Hendra virus glycoprotein mRNA LNP vaccine (10 µg [VAX LO] or 30 µg [VAX HI]) in NiV challenge show robust anti–NiV-specific antibody responses. (A), Adjusted absorbance readings from 4-fold dilutions of hamster plasma in a NiV-specific immunoglobulin G (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Horizontal bars represent means for survivor groups and non-survivors (from all groups); vertical lines, standard deviations; dotted line, cutoff value for diagnostic determination of a positive sample. *P < .01; †P < .001 (2-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with Tukey multiple comparisons test). (B), NiV neutralization by plasma samples from individual hamsters. Reciprocal plasma dilutions in which hamster plasma completely neutralized 200 times the median tissue culture infective dose (TCID50) of NiV genotype M (NiV M) across 4 replicates were plotted according to group-specific indications. Horizontal bars represent geometric means for survivor groups and non-survivors (from all groups); vertical lines, standard deviation; dotted line at 10, limit of detection for virus neutralization assay. Plasma samples with undetectable neutralizing activity were plotted as having a titer of 5. Owing to insufficient samples, only 3 plasma samples were tested from recipients of phosphate-buffered saline vehicle control. *P < .01; †P < .001 (1-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons Kruskal-Wallis test). (C), Immunofluorescence assay depicted with representative micrographs from a VAX HI survivor. Plasma samples collected from representative NiV challenge survivors, diluted 1:40 in phosphate-buffered saline with 5% skim milk, were incubated with either NiV nucleoprotein (NiV N), NiV attachment glycoprotein (NiV G), or mock-transfected CHO-K1 cells. Goat anti-hamster Dylight 488–conjugated antibodies were used to detect primary hamster antibodies, and nuclei were stained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Scale bar represent 100 µm.