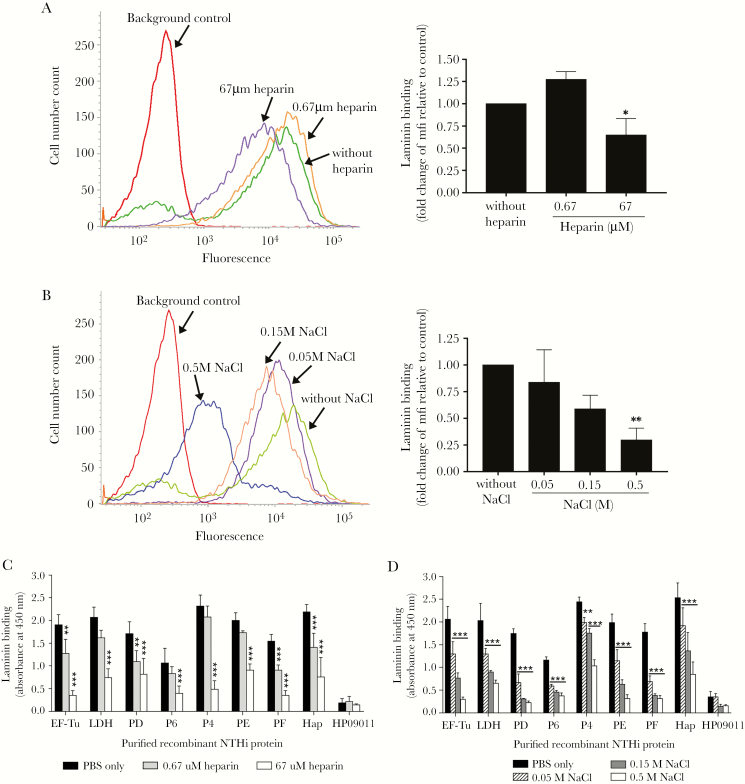
Figure 6.
Characterization of heparin inhibition and ionic interaction in laminin binding of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi). (A and B) Direct protein-binding assay of NTHi 3655 with lamininmur in the presence of heparin and NaCl as measured by flow cytometry. (A) Binding of NTHi 3655 with lamininmur (25 nM) that had been preincubated with various concentrations of heparin (0.67 and 67 μM). (B) Interaction of NTHi 3655 with lamininmur (25 nM) in the presence of increasing concentrations of NaCl (0.05–0.5 M). Impaired bacterial binding to laminin was observed in the presence of 67 μM heparin or NaCl at ≥50 mM. Left panels in A and B show representative histograms of three independent experiments, and to the right fold change of mean fluorescence intensity (mfi) of laminin binding in the presence of heparin or NaCl relative to the control without inhibitors is shown. (C and D) Inhibition of the laminin-NTHi laminin-binding proteins (Lbps) interaction by heparin and NaCl as analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Immobilized recombinant NTHi Lbps (EF-TuM1-K394, LDHM1-L381, PDS19-K364, P6S21-Y153, Rib30sM1-E125, P4G22-K274, PE22-160, PF12-293, and HapE523-L1036) were loaded with the following: (C) lamininmur (10 nM) that was preincubated with heparin (0.67 and 67 μM) or (D) lamininmur (10 nM) in the presence of NaCl (0.05–0.5 M). Heparin at ≥0.67 μM or NaCl at ≥50 mM disrupted the interaction of laminin with all NTHi Lbps. HP09011 was included as negative control. In A–D, data represent mean values of three independent experiments and error bars indicate standard deviations. Statistically significant differences in laminin binding between conditions with and without heparin or NaCl were calculated by one-way (for A and B) and two-way ANOVA (for C and D). In D, horizontal bars indicate similar significance of statistical differences within group data, when compared with the control without additional NaCl (phosphate-buffered saline only). *, P ≤ .05; **, P ≤ .01; and ***, P ≤ .001.