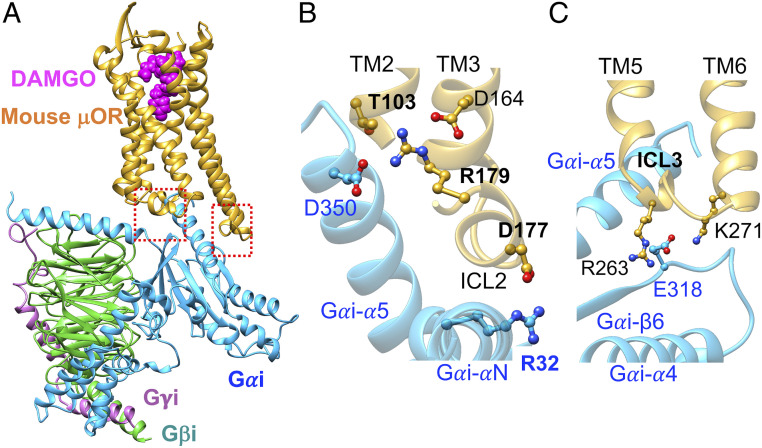
Fig. 3.
Activated Gi protein binds to activated mouse μOR in the same fashion as βarr2 couples to pp-μOR. (A) Well-optimized Gi-mouse-μOR-DAMGO complex obtained from MD simulation (15), starting from the recent cryo-EM (30). (B) The polar anchor from R32Gαi to D177ICL2 (equivalent to D179 in the human μOR). This salt bridge creates a network of polar interactions from the Gαi-α5 helix to the ICL2 and the cytosolic end of TM2, which is similar to the network that emerges from βarr2 coupling to the pp-μOR. (C) The polar anchors between Gi protein and μOR: from E318 to R263ICL3 (equivalent to R265 in the human μOR) and K2716.26 (equivalent to K273 in the human μOR). These anchors show that Gi protein and βarr2 compete for the same binding site in the μOR, even though their recruitment results to totally opposite outcomes.