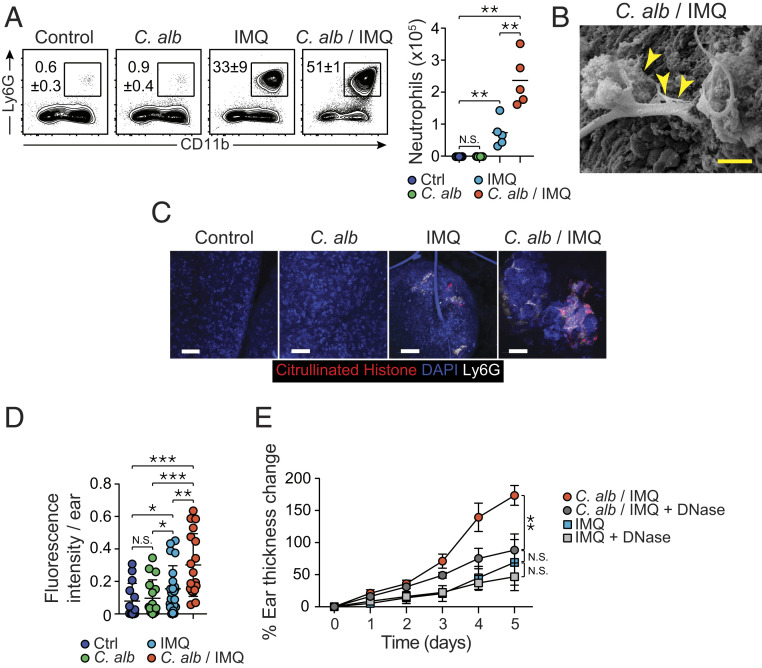
Fig. 3.
Preexposure to C. albicans leads to enhanced neutrophil response and NETs-mediated pathology. (A) Representative flow plots showing frequencies of live neutrophils in the ear pinnae of naïve control (Ctrl), C. alb-, IMQ-, and C. alb/IMQ-treated SPF mice (Left). Absolute numbers of live neutrophils in the ear pinnae from the different groups of mice (Right). (B) Representative image of the surface of the ear pinnae from C. albicans/IMQ-treated SPF mouse obtained by scanning electron microscope. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) Arrows indicate web-like structures on the surface of the ear. (C) Representative images of high magnification of whole mouse ear pinnae sections from untreated control SPF mice, C. alb-, IMQ-, and C. alb/IMQ-treated SPF mice showing DAPI (blue), citrullinated histone H3+ cells (red), and Ly6G (white). (Scale bars, 50 μm.) (D) NETs frequency evaluated by fluorescence intensity of citrullinated histone H3 per ear pinnae from untreated control (Ctrl) SPF mice, C. alb-, IMQ-, and C. alb/IMQ-treated SPF mice. (E) Time course of percentage of ear thickness change relative to baseline at day 0 from IMQ- and C. alb/IMQ-treated SPF mice and from IMQ- and C. albicans/IMQ-treated SPF mice following DNase treatment (IMQ + DNase and C. alb/IMQ + DNase). Results are representative of two to three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; N.S., not significant.