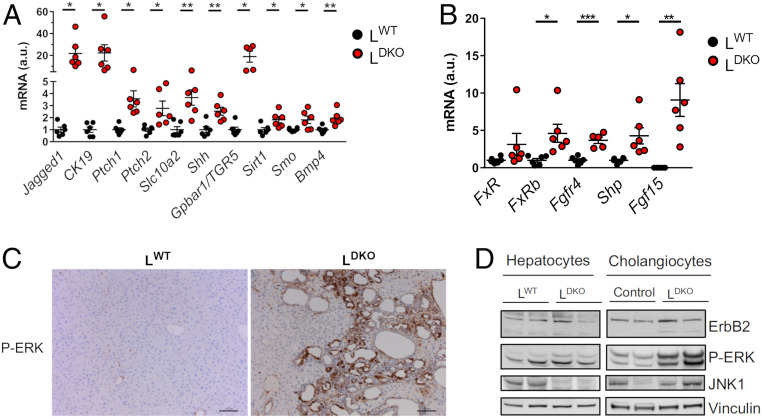
Fig. 3.
ERK pathway activation accompanies the development of cholangiocarcinoma induced by hepatic JNK deficiency. (A) The expression of genes related to cholangiocytes proliferation was evaluated by RT-PCR in 14-mo-old LWT and LDKO mice and normalized to the amount of 18S RNA in each sample (mean ± SEM; n = 5–6). Student’s t test differences between LDKO and LWT are indicated (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (B) The expression of genes related to the nuclear factor FXR (Fxr, Fxrb, Shp, Fgfr4) and Fgf15 was measured by quantitative RT-PCR in LWT and LDKO liver from mice at age 6 mo (mean ± SEM; n = 5–6) normalized to the amount of Actb mRNA in each sample. Student’s t tests between LDKO and LWT are indicated (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (C) Representative liver sections of LDKO and LWT mice (age 10 mo) stained with phospho-ERK. (Scale bar, 100 µm.) (D) Comparative protein expression of ErbB2, phospho-ERK, and JNK1 in hepatocytes and cholangiocytes in LWT and LDKO mice was evaluated by immunoblot analysis. Vinculin was used as a loading control.