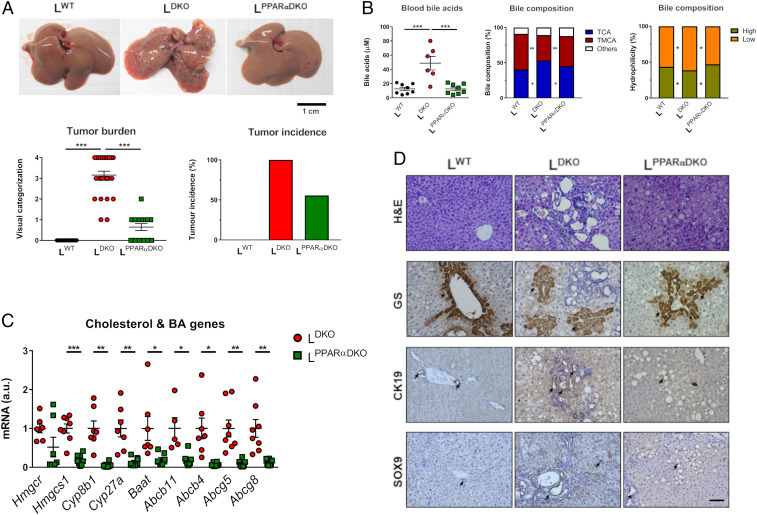
Fig. 4.
PPARα deficiency reduces liver cancer induced by hepatic JNK deficiency. (A) Representative livers, tumor burden, and incidence in 11-mo-old LWT, LDKO, and LPPARαDKO mice (mean ± SEM; n = 14 ∼ 25). (B) The amount of bile acid in the blood was measured (mean ± SE; n = 7–11). The composition of bile fluid collected from the gall bladder was examined. Two-way ANOVA differences between LPPARαDKO, LDKO, and LWT are indicated (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (C) The expression of genes related to cholesterol synthesis (Hmgcr and Hmgcs1), BA synthesis, and transporters (Cyp27a1, Baat, Cyp27a, Cyp8b1, Abcb11, Abcb4, Abcg5, Abcg8) was measured by quantitative RT-PCR (mean ± SEM; n = 5–8) normalized to the amount of Actb mRNA in each sample. Two-way ANOVA differences between LDKO and LPPARαDKO are indicated (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (D) Representative liver sections of 10-mo-old LWT, LDKO, and LPPARαDKO mice stained with GS, Cytokeratin 19 (CK19), and Sox9. (Scale bar, 100 µm.)