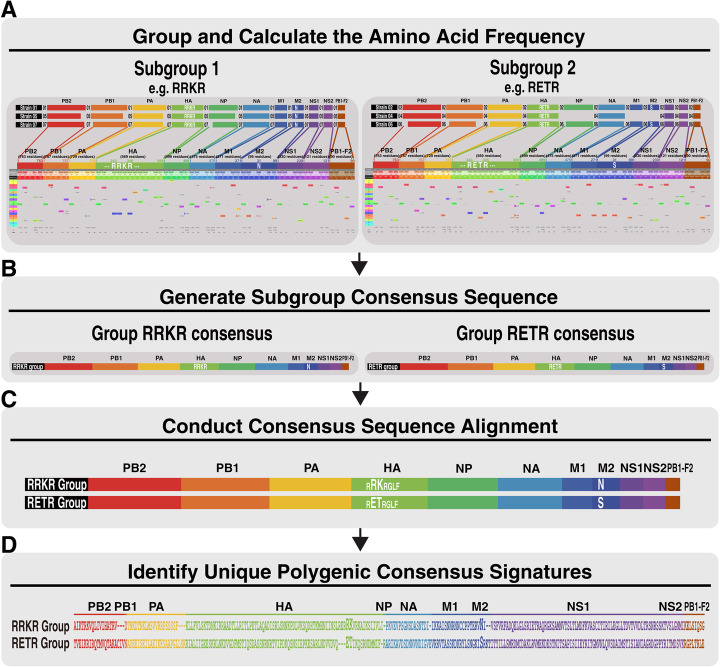
Fig. 3.
Identification of group-specific polygenic consensus signatures by FluCG. The polygenic consensus signatures are determined as follows: a FluCG groups viral strains into different subgroups (e.g. RETR and RRKR groups). The consensus sequence of each subgroup is determined by computing a table of 20 amino-acid substitutions to choose the most representative amino acid at each position of the whole genome. The stop codon is denoted as “X” and the deleted residue is denoted as “-”. b One consensus sequence from each subgroup is determined. c FluCG aligns two group consensus sequences and identifies the signature that is unique, to distinguish between the two consensus sequences. d Text in different colors represents different proteins that compose the polygenic consensus signatures