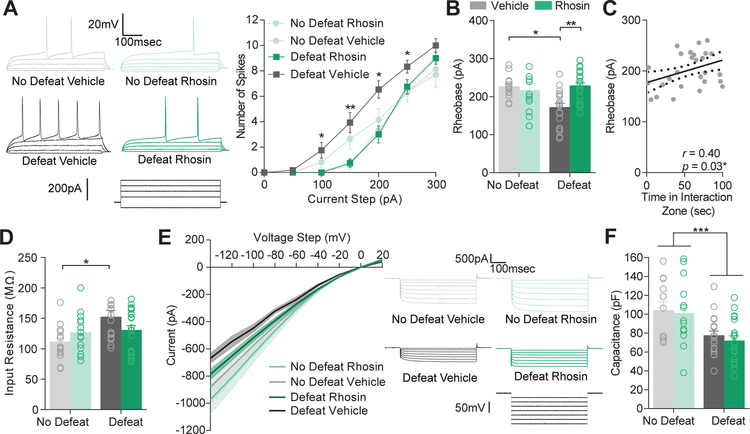
Figure 3. Rhosin blocks stress-induced hyperexcitability in NAc D1-MSNs.
(A) Current (−50 to 300 pA) was injected in to NAc D1-MSNs from non-defeat or defeat mice treated with vehicle or Rhosin. Representative traces with current injection (50–200 pA) from each condition are shown. Rhosin blocked hyperexcitability observed in defeat mice treated with vehicle (P<0.0001). (B) Reduced rheobase is prevented by Rhosin treatment (P<0.01; (C) Rheobase positively correlates with time spent in the interaction zone (P<0.05). (D) Enhanced input resistance is blocked by Rhosin (P<0.05). (E) Evoked plateau currents (the point at which current stabilizes in response to a negative voltage pulse) from voltage clamp steps (−140 to 20mV) were smaller in defeat vehicle mice but not mice treated with Rhosin (P<0.0001). (F) Capacitance was significantly reduced in all defeat animals (Interaction P>0.05; Main effect of defeat P<0.001; for all experiments N/n= 4–7/12–20). For exact statistics see Supplemental Table 1.