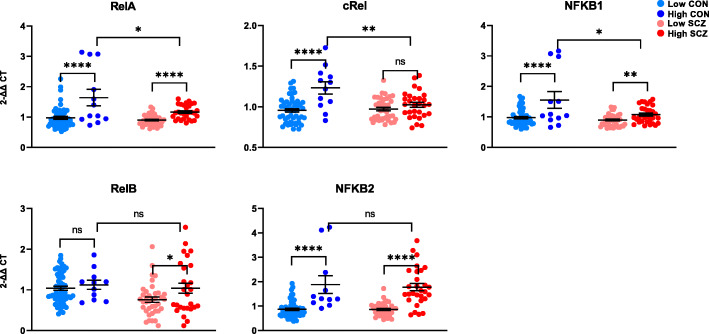
Fig. 5.
Gene expression of NF-κB subunits and subunit precursors in the post-mortem dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of controls (CON) and people with schizophrenia (SCZ). Diagnostic groups were stratified based on neuroinflammatory biotype at time of death (low neuroinflammation or high neuroinflammation). RelA, cRel, and NFKB1 mRNAs were increased in high neuroinflammation groups in both diagnoses; however, high neuroinflammation controls had significantly higher expression of all three transcripts compared to high neuroinflammation patients. RelB expression was associated with neuroinflammation only in patients and was decreased in schizophrenia compared to controls overall (p = 0.013). NFKB2 mRNA was upregulated in high neuroinflammation relative to low neuroinflammation and did not differ between non-schizophrenic controls with neuroinflammation and patients with neuroinflammation. Error bars depict standard error of the mean. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001, ns = not significant