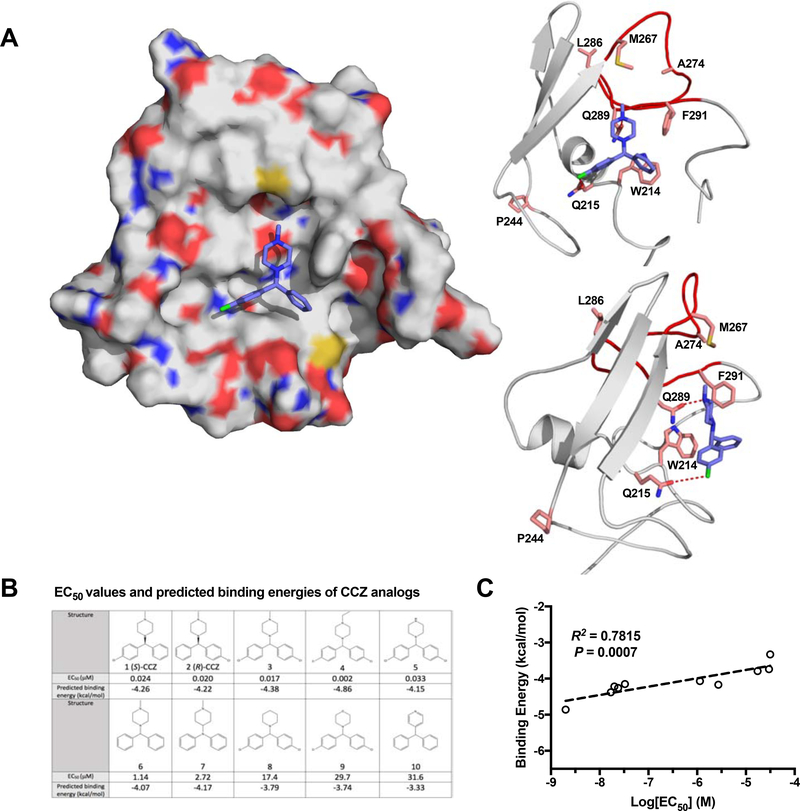
Figure 6. Molecular modelling of CCZ binding to HCV E1 protein.
A. Predicted binding model of (S)-CCZ with E1. The (S)-CCZ fits into a hydrophobic pocket of the space-filling model of E1 on the left. On the right, interactions of (S)-CCZ with various key amino acid residues, as identified by the mutagenesis studies, are shown in a ribbon model. The hydrogen bond between Q289 and the N atom of the piperazine, and a halogen bond between Q215 and the chlorophenyl group of (S)-CCZ provide significant stabilization. B. EC50 values and predicted binding energies of CCZ analogs. The EC50 values of 10 structurally related CCZ analogs published previously were compared with their respective predicted binding energies. C. The EC50’s of 10 CCZ analogs (A) were plotted against their respective binding energies predicted based on various intermolecular interactions (e.g., hydrogen bonds, electrostatic interactions, pi-pi stacking, etc.). The anti-HCV activities of the CCZ analogs correlate well with the binding energies (R2 = 0.7815, P = 0.0007).