Figure 1.
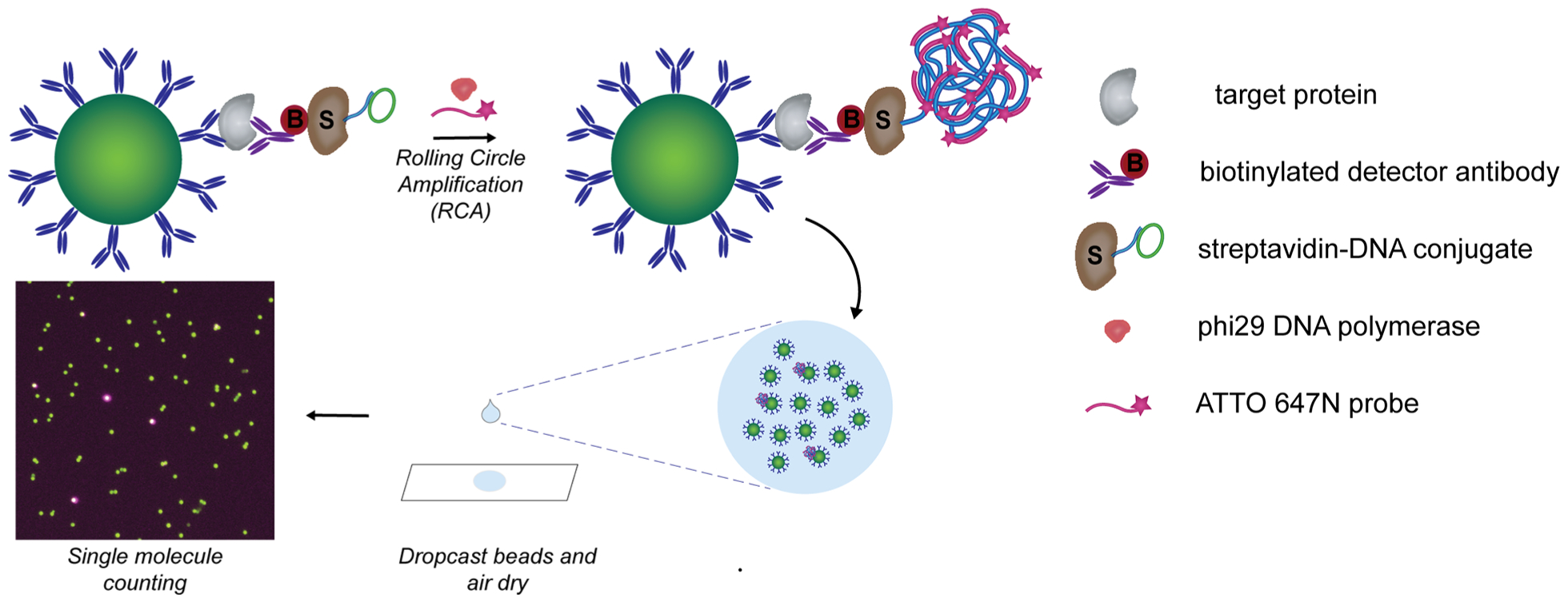
Schematic of dropcast single molecule assays. Upon formation of single immunocomplex sandwiches on antibody-coated paramagnetic beads and labeling with a streptavidin-DNA conjugate, rolling circle amplification (RCA) is performed on the beads to generate a long concatemer attached to each immunocomplex. Fluorescently labeled DNA probes are hybridized to the concatemer during RCA to produce a localized fluorescent signal on beads carrying a full immunocomplex sandwich. After RCA, the beads are concentrated, dropcast onto a microscope slide, and allowed to dry to form a monolayer film. Single target molecules are counted by fluorescence imaging of the dropcast film and counting “on” and “off” beads.
