Figure 1. Mechanism of Mu transposition, and initial genomic location of Mu prophages.
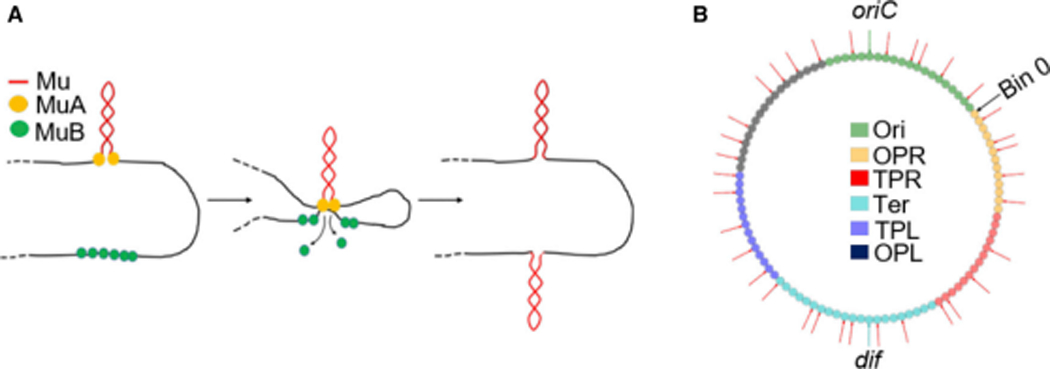
(A) Simplified cartoon of Mu replicative transposition. (B) Locations on the E. coli genome of the 35 Mu prophages (red arrows) used in this study. oriC and dif are sites where replication initiates and terminates. The genome was partitioned into 100 equally sized bins (0–99; small circles). The different bin colors refer to the regions shown in the legend. The original NS regions flanking Ori are named Ori proximal left (OPL) and Ori proximal right (OPR), and the original Left and Right regions flanking Ter, Ter proximal left (TPL) and Ter proximal right (TPR), to avoid confusion when talking about the general left and right arms of the chromosome.
