Figure 7. Lymphoid organ disorder and autoimmune manifestations caused by TRAF3-deficiency are rectified by limiting BCR repertoires or attenuating BCR signaling strength.
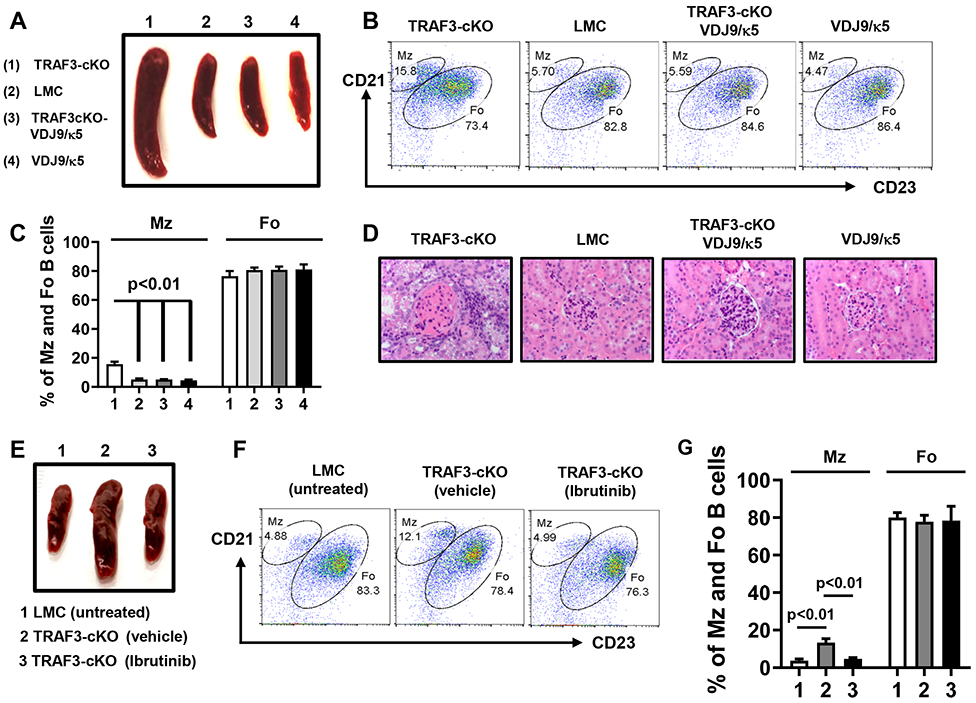
(A to D) TRAF3-cKO mice were crossed with VDJ9/κ5 mice to generate TRAF3-cKO-VDJ9/κ5 mice. (A) Representative image of mouse spleens with indicated genotypes and indicated number of mice examined in total: (1) TRAF3-cKO (n=24); (2) LMC (n=63); (3) TRAF3-cKO-VDJ9/κ5 (n=5); and (4) VDJ9/κ5 (n=10) (8-12 weeks old). (B) Flow data showing the profiles of MZ and FO B cells in mice with indicated genotypes. B cells were gated for B220+IgM+ double positive population. (C) Quantification of the percentage of MZ and FO B cells in mice with indicated genotypes as labeled in (A) (n=5/group). (D) Representative H&E staining of kidney samples. Magnification 40×. (E) Representative image of mouse spleens with indicated genotype and treatment (group 1-3, n=5/group, 12 weeks old). (F) Representative flow data showing the profiles of MZ and FO B cells. B cells were gated for B220+IgM+ double positive population. (G) Quantification of the percentage of MZ and FO B cells in mice with indicated genotype and treatment as labeled in (E) (n=5/group). TRAF3-cKO, CD19Cre-Traf3f/f. Data are representative of 3-6 independently repeated experiments.
