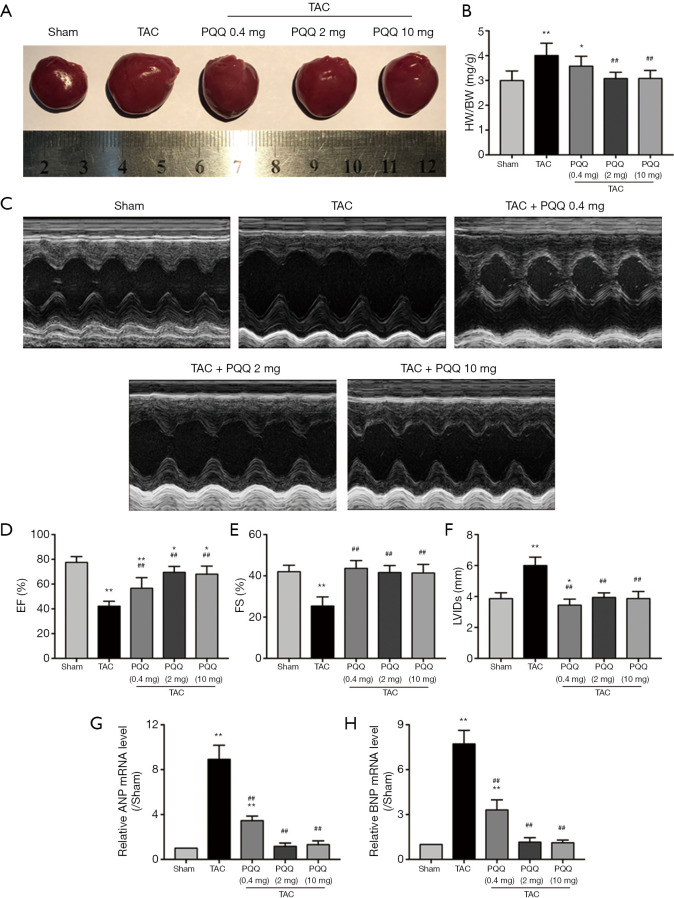
Figure 1.
PQQ could delay or prohibit CHF development. The optimal dose of PQQ for intragastric administration to rats was determined. (A) Heart sizes of rats treated with or without PQQ (0.4, 2 and 10 mg/kg) administered intragastrically 12 weeks after TAC or sham surgery. (B) Ratio of heart weight and body weight (HW/BW). (C) M-mode echocardiographic images of the left ventricle along the left parasternal long axis. (D,E,F) Heart failure parameters as determined by echocardiography (left ventricular ejection fraction, left ventricular fraction shortening and left ventricular internal diameter at end-systole). (G,H) Real-time PCR quantitative analysis of heart failure markers (ANF and BNP) in rat left ventricular tissue. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P<0.05; **P<0.01 vs. sham. ##P<0.01 vs. TAC. PQQ, pyrroloquinoline quinone; CHF, chronic heart failure; TAC, transaortic constriction; ANF, atrial natriuretic peptide; BNP, brain natriuretic peptide.