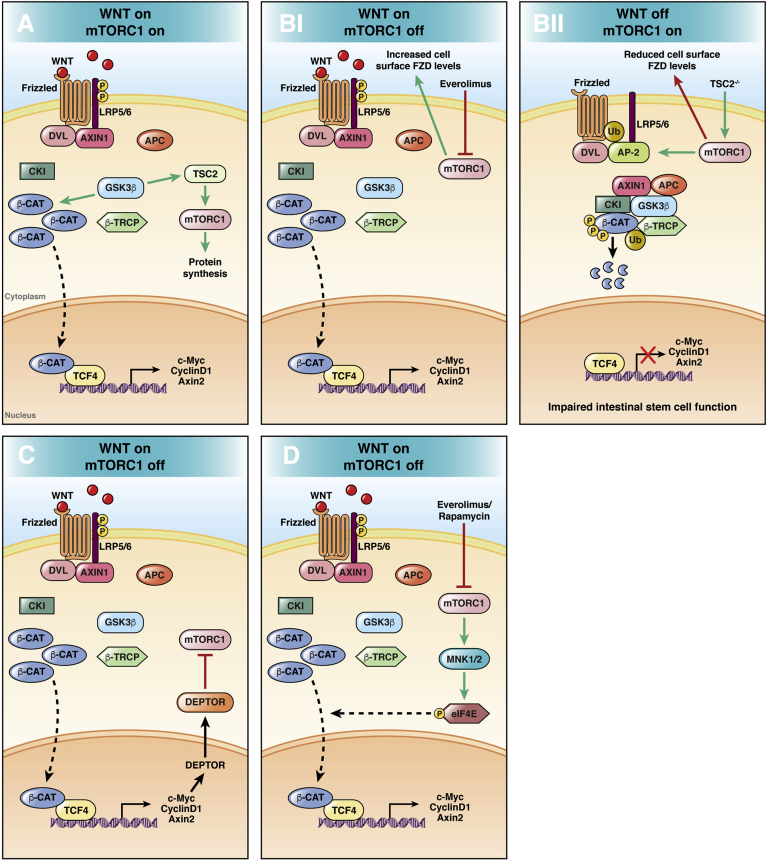
Figure 1.
Main mechanisms of Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 pathway interconnections. (A) The Wnt/β-catenin pathway modulates transcription through β-catenin and translation via mTORC1 regulating GSK3β activity.96 (Bi) mTORC1 inhibition by the rapalog everolimus induces Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation by increasing the expression of FZD receptor levels with a mechanism dependent on DVL. (Bii) Activated mTORC1 promotes the association between DVL and the clathrin Adaptor protein 2 (AP-2) adaptor with a consequent reduction of FZD expression levels, with a negative regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.116 (C) Wnt/β-catenin signaling switches off the mTORC1 cascade by inducing its negative regulator DEPTOR.117 (D) Inhibited PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 pathway leads to increased eIF4E phosphorylation via MNK.124 Phosphorylated eIF4E is associated with β-catenin nuclear translocation and signaling activation.127 β-CAT, β-catenin; β-TRCP, Beta-transducin repeat containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase.