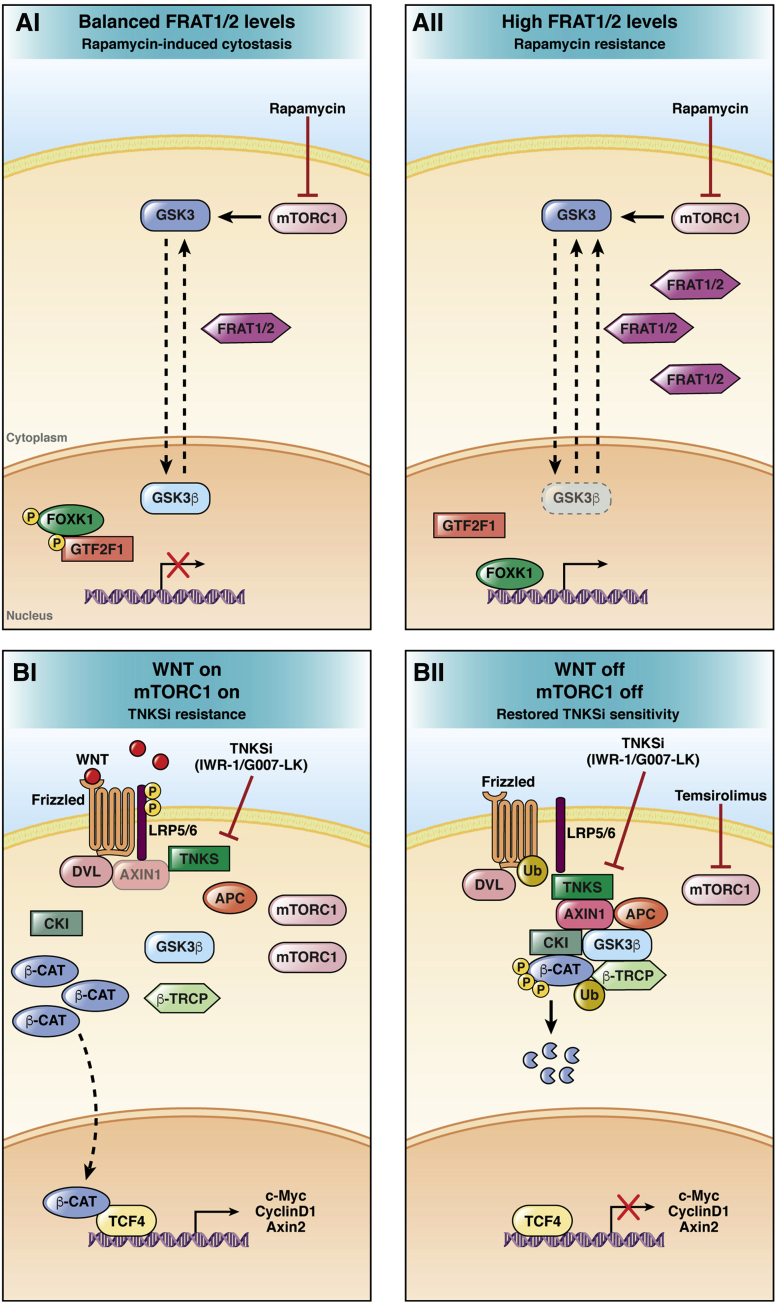
Figure 2.
Resistance mechanisms to rapamycin and TNKSi. (Ai) mTORC1 inhibition promotes GSK3β nuclear translocation. Nuclear GSK3β mediates rapamycin-induced cytostasis by increasing the phosphorylation of Forkhead Box K1 and General Transcription Factor IIF Subunit 1. (Aii) In conditions of high cellular levels of the GSK3β nuclear exporter Frequently rearranged in advanced T-cell lymphomas 1/2 (FRAT 1/2), upon mTORC1 inhibition, nuclear GSK3β levels are not sufficient to induce cytostasis leading to rapamycin resistance.113,114 (Bi) mTORC1 induction is associated with TNKSi resistance and persistent Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation. (Bii) mTORC1 activity reduction by temsirolimus restores the sensitivity to TNKSi, leading to Wnt/β-catenin down-regulation.144 β-CAT, β-catenin; β-TRCP, Beta-transducin repeat containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase; CKI, Casein Kinase I.