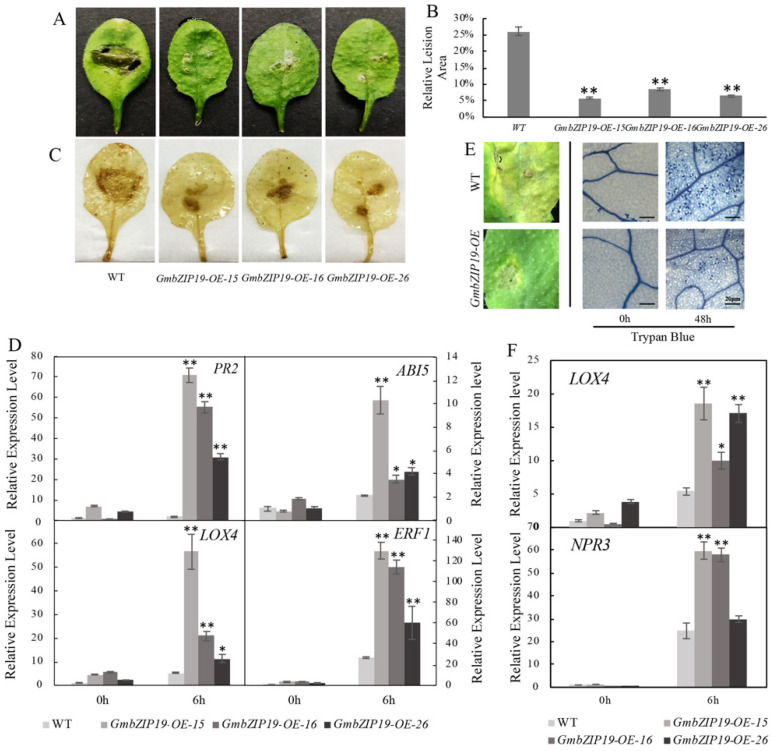
Figure 3.
Overexpression of GmbZIP19 confers improved disease resistance against S. sclerotiorum and Pseudomonas syringae. (A) The phenotype of GmbZIP19-OE lines and WT after S. scleroterium infection. (B) The relative lesion area of GmbZIP19-OE lines and WT under S. scleroterium infection. Error bars indicate ± SD (n = 5 leaves). (C) The DAB staining result (accumulation of H2O2 in leaves) of GmbZIP19-OE lines and WT after S. scleroterium infection. (D) qPCR analysis of transcription levels in GmbZIP19-OE transgenic and WT plants after S. scleroterium infection. (E) The phenotype and trypan blue staining result of GmbZIP19-OE and WT plants under Pseudomonas syringae infection. Bar = 20 μm. (F) qPCR analysis of transcription levels in GmbZIP19-OE transgenic and WT plants after pst. DC3000 infection. The error bars were obtained from multiple replicates of the RT-qPCR and indicate ±SD (n = 3 replicates). Asterisks indicate significant differences for the indicated comparisons based on a Students’ t-test (** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05).