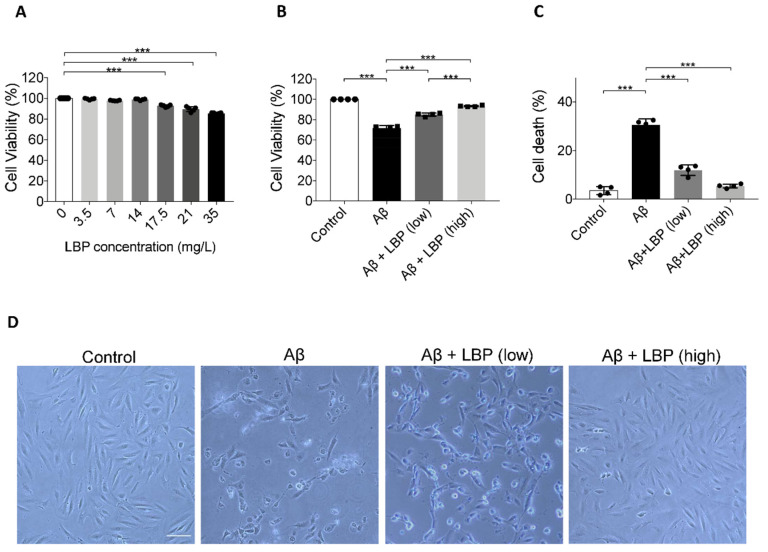
Figure 2.
The effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on ARPE-19 cell viability and morphology. (A) ARPE-19 cell viability after Lycium barbarum polysaccharides (LBP) treatment at various concentrations were determined by CCK-8 assay. No significant changes were observed for LBP treatment up to 14 mg/L. However, cell viability started to decrease when LBP was administered at 17.5 up to 35 mg/L. (n = 4, ***p < 0.001). (B) Exposure to Aβ1-40 oligomers decreased ARPE-19 cell viability (column 2). Administration of LBP at both low (3.5 mg/L) and high (14 mg/L) dosage were able to reverse the decreased cell viability imposed by Aβ1-40 oligomers (columns 3 and 4) (n = 4, ***p < 0.001). (C) Protective effects of LBP at low and high dosages were confirmed by trypan blue assay, which revealed that the ARPE-19 cell death rate was decreased by LBP treatment (n = 4, ***p < 0.001). (D) The morphological changes of ARPE-19 cells upon Aβ1-40 oligomers exposure with/without LBP treatment were examined by light microscopy. There was a decrease in cell number together with rounded cells and debris after Aβ1-40 oligomers exposure. The cells retained their normal morphology with LBP treatment (scale bar = 100 µm).