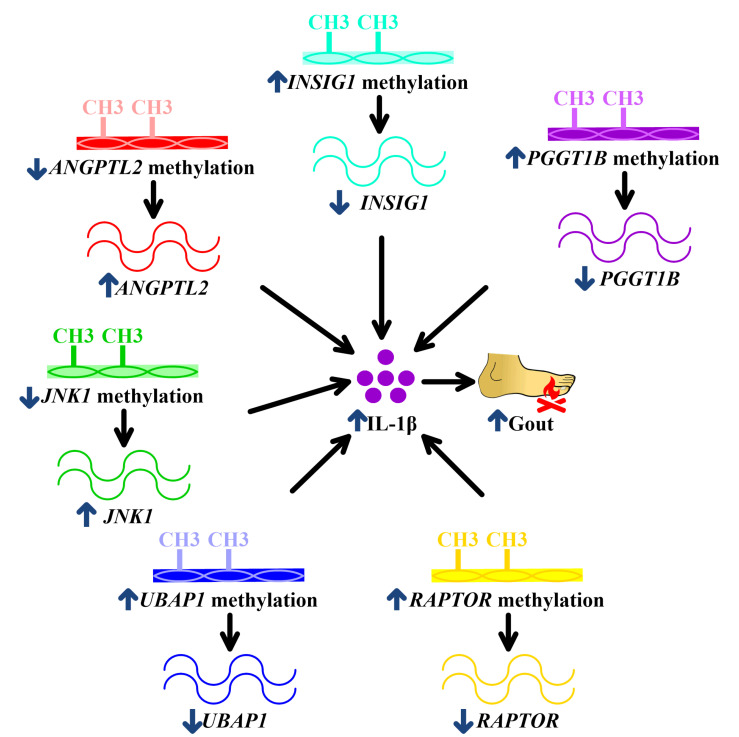
Figure 5.
Potential mechanisms underlying associations of PGGT1B, INSIG1, ANGPTL2, JNK1, UBAP1, and RAPTOR methylation with gouty inflammation. PGGT1B hypermethylation in gout decreases PGGT1B, INSIG1 hypermethylation in gout reduces INSIG1, ANGPTL2 hypomethylation enhances ANGPTL2, hypomethylated JNK1 increases JNK1, UBAP1 hypermethylation downregulates UBAP1, and hypermethylated RAPTOR represses RAPTOR. All of these culminate in augmented IL-1β production, facilitating gouty inflammation. The blue arrows mean the change of methylation or expression or development of gout. The black arrows mean the consequence of methylation or expression alterations.