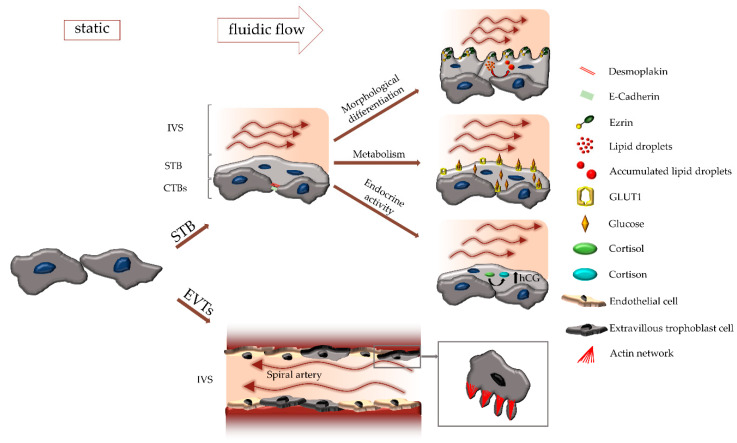
Figure 2.
Influence of fluidic flow on different trophoblast subtypes. Fluidic flow regulates differentiation and physiology of both, the syncytiotrophoblast (STB) and extravillous trophoblasts (EVTs). During syncytialization, cell-cell contact proteins, such as desmoplakin and E-cadherin are downregulated, and the structural protein ezrin relocalizes from the basal to the apical side. Formation and appearance of microvilli on the apical surface as well as accumulation of lipid droplets in the STB are influenced by fluidic flow. Moreover, fluidic flow affects expression and localization of GLUT1, secretion of hCG as well as conversion of cortisol to cortisone. In the EVT subpopulation, formation of filopodia, and hence migratory behavior is regulated by fluidic flow as well.