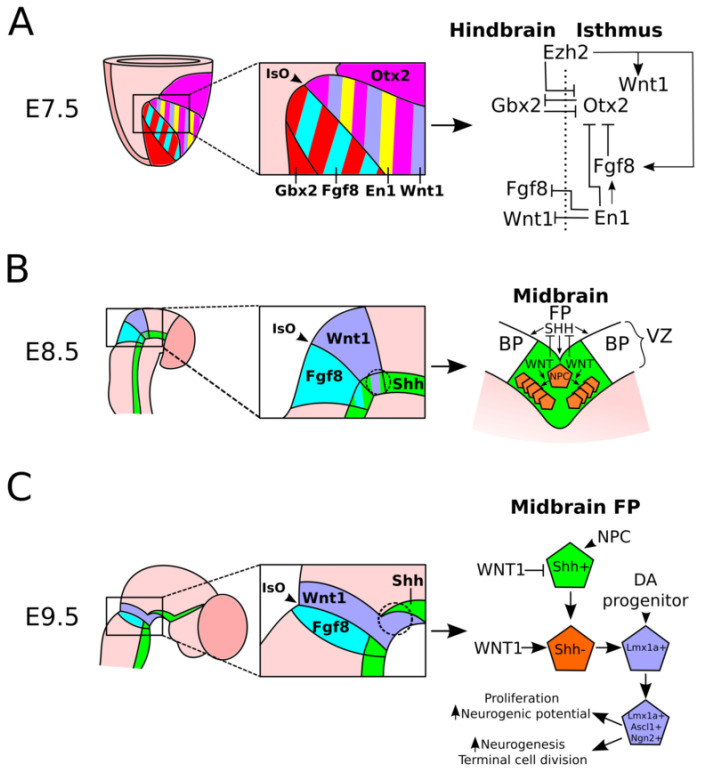
Figure 1.
Patterning of the isthmus and midbrain region during early stages of development. (A): Schematic representation of the establishment of the isthmus during early stages of development. Around E7.5, the isthmus is established by the reciprocal expression of Gbx2 and Otx2. This leads to expression of Fgf8 in the isthmus, regulated by the expression of En1 in the midbrain. En1 inhibits the expression of Wnt1 in the hindbrain, allowing for exclusive expression of this signaling molecule in the isthmus and midbrain area. The broadly expressed gene Ezh2 positively regulates the expression of Wnt1 and Fgf8 in the isthmus and midbrain. (B): Schematic representation of the patterning of the FP by SHH and the increase in the neural progenitor cells (NPC) pool in the midbrain by WNT at early stages of development. Around E8.5, SHH-signaling in the FP of the midbrain allows for correct patterning of the FP and DA progenitors and WNT-signaling, inhibiting SHH signaling, for the expansion of the NPC pool in the VZ of the embryonic midbrain. (C): Schematic representation of the specification of DA progenitors from NPCs in the VZ of the mesodiencephalic FP. Expression of Shh in NPCs is inhibited by WNT-signaling in the midbrain area, which simultaneously activates the transition of NPCs to DA progenitors that express Lmx1a, Ascl1, and Ngn2. Expression of Ascl1 in DA progenitors enhances proliferation and increases neurogenic potential, whereas Ngn2 increases neurogenesis after terminal cell divisions.