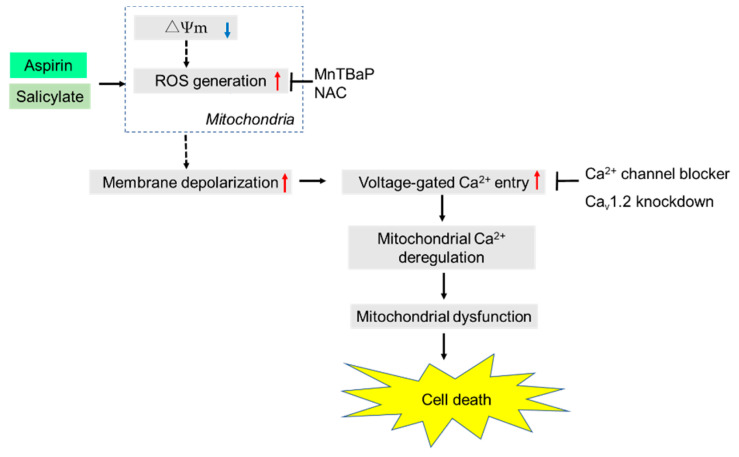
Figure 7.
A schematic summary of the present study. Both aspirin and salicylate induce rapid and persistent depolarization, and ROS mediate the effect. The ROS may be primarily generated by the electron transport chain through loss of ΔΨm, as we previously showed with electron transport chain inhibitors, rotenone, antimycin A, and FCCP [20]. In turn, the depolarization without repolarization leads to excessive activation of VGCCs, including Cav1.2, thereby leading to Ca2+m deregulation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cell death.