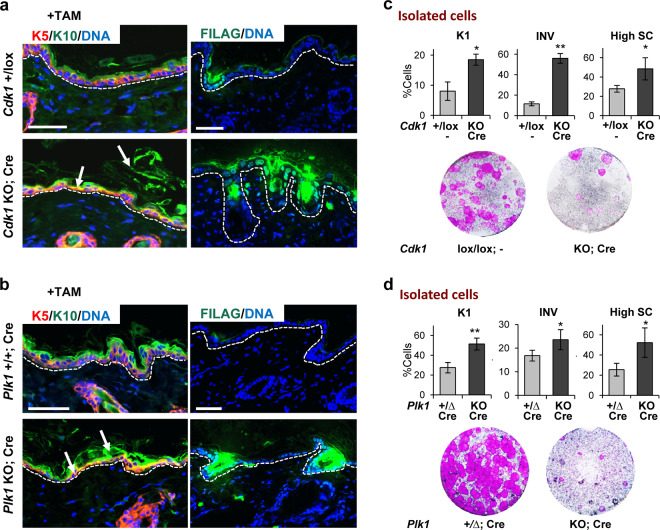
Fig. 3. The loss of Cdk1 or Plk1 results in premature basal terminal differentiation.
a Representative double immunofluorescence of back epidermis of control mice (Cdk1+/lox;−) or KO mice (Cdk1 KO; Cre) upon TAM (8 days) treatment for squamous markers keratin K5 (red) and keratin K10 (green) or filaggrin (FILAG, green). DNA in blue (DAPI). Broken line for the basement membrane. Scale bars: 50 μm. b Representative double immunofluorescence as in a of back epidermis of control mice (Plk1+/+; Cre) or KO mice (Plk1 KO; Cre) upon TAM (6 days) treatment. c Bar histograms display the percent of involucrin (INV) positive cells, keratin K1 positive cells or cells with high scatter (High SC) from mice in a measured by flow cytometry. Bottom: representative clonogenic capacity of cells from mice as in a. d Bar histograms display the percent of involucrin (INV) positive cells, keratin K1 positive cells or cells with high scatter (High SC) from mice as in b 7 days after treatment measured by flow cytometry. Bottom: representative clonogenic capacity of cells as in b 7 days after treatment measured. **P < 0.01 *P < 0.05. Cdk1 control mice do not have CRE recombinase (−). The deletion of the floxed sequences is represented by Δ. Data are mean ± SD of 2–3 animals per group (N = 2–3) and three independent experiments. See also Supplementary Fig. 2.