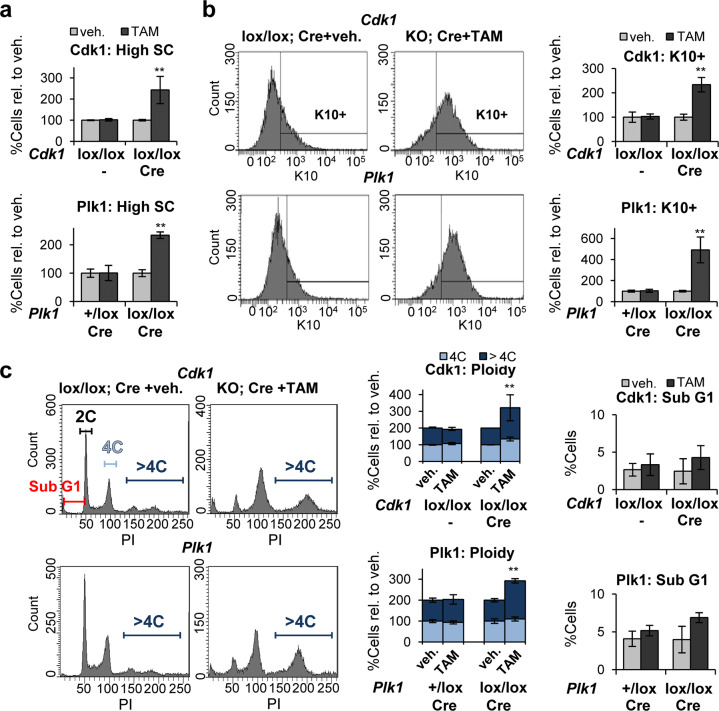
Fig. 4. Inactivation of Cdk1 or Plk1 in freshly isolated cells induces squamous differentiation.
a Percent of cells with high-scatter parameters (high SC), in Cdk1 control cells (Cdk1lox/lox;−) or Cdk1lox-cre cells (Cdk1lox/lox; Cre) 3 days after treatment with TAM or with vehicle (veh.) only (top) or, Plk1 control cells (Plk1+/lox; Cre) or Plk1lox-cre cells (Plk1lox/lox; Cre) 4 days after treatment with TAM or with veh only (bottom), relative to keratinocytes treated with veh. b Representative flow-cytometry histograms for the differentiation marker keratin K10 (K10+, positive cells according to negative isotype antibody control, not shown). Bar histograms show the percent of K10 positive cells as in a relative to keratinocytes treated with veh. c Representative flow-cytometry analyses of DNA content. Bar histograms: percent of 4C cells (G2/M + tetraploids), >4C cells (Polyploid) or in the Sub-G1 fraction of the cell cycle (as measured by PI), as in a and relative to keratinocytes treated with veh. **P < 0.01. Cdk1 control mice do not have CRE recombinase (−). Data are mean ± SD of duplicate or triplicate samples (n = 2 or n = 3) of at least two mice per group (N = 2) and three independent experiments. See also Supplementary Figs. 3, 4.