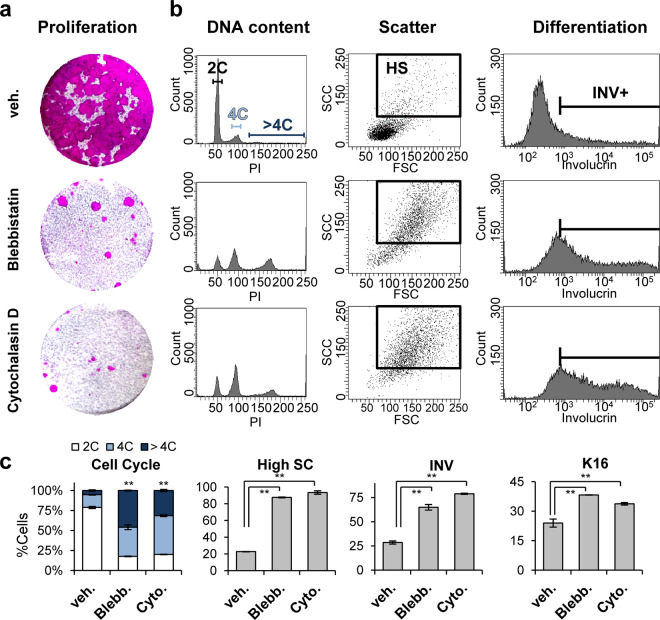
Fig. 5. Inhibition of cytokinesis in human epidermal cells triggers squamous differentiation.
Primary cells from human epidermis were treated with vehicle (veh.), blebbistatin (Blebb.) or cytochalasin (Cyto.) for 48 h. a Clonogenic capacity of cells drug-released and plated (3000 cells per well in triplicate samples) after treatment as indicated. b Representative flow-cytometry analyses for DNA content, morphology (light scattering) and expression of the differentiation marker involucrin (INV+, positive cells), as indicated. c Bar histograms: percent of 2C (G1, dyploid), 4C (G2/M + tetraploids) or >4C (polyploid) cells as measured by PI; percent of cells with high light scatter features (high SC); percent of INV+ cells; or percent of keratin K16 positive cells, as indicated. **P < 0.01. Data are mean ± SD of triplicate samples (n = 3) and three independent experiments. See also Supplementary Fig. 4.