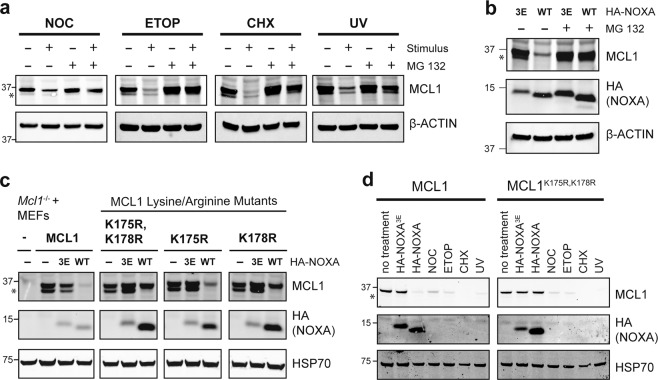
Fig. 1. Lysines 175 and 178 of MCL1 are critical for its degradation triggered by the BH3-only protein NOXA, but not by other stimuli.
a A variety of stress stimuli provoke MCL1 degradation by the proteasome. Bax−/−Bak−/− MEFs were exposed to nocodazole (NOC; 400 ng/mL for 16 h), etoposide (ETOP; 50 μM for 16 h), cycloheximide (CHX; 50 μg/mL for 16 h), or UV irradiation (200 J/m2; then cultured for 4 h). Where indicated, the cells were also cultured with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (10 μM). b NOXA promotes MCL1 degradation by the proteasome. Bax−/−Bak−/− MEFs were engineered to express HA-NOXA (WT) or HA-NOXA3E (3E), a mutant that does not bind MCL1 [21]. Where indicated, the cells were also cultured with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (10 μM) for 16 h. c Lysines 175 and 178 of mouse MCL1 are critical for NOXA to trigger its degradation. Mcl1−/−Bax−/−Bak−/− MEFs were engineered to express WT MCL1 or the indicated MCL1 mutants together with HA-NOXA or HA-NOXA3E. d Unlike NOXA-induced degradation, other stress stimuli degrade MCL1 independently of K175 and K178. Mcl1−/−Bax−/−Bak−/− MEFs were engineered to express WT MCL1 or MCL1K175R,K178R together with HA-NOXA or HA-NOXA3E, or exposed to nocodazole (NOC; 400 ng/mL for 16 h), etoposide (ETOP; 50 μM for 16 h), cycloheximide (CHX; 50 μg/mL for 16 h), or UV irradiation (200 J/m2; then cultured for 4 h). Asterisks denote MCL1Matrix, a form of the protein that has undergone N-terminal proteolysis associated with import into the mitochondrial matrix [67, 68]. The absence of MCL1Matrix from cells expressing wild-type HA-NOXA suggests that the binding of NOXA to MCL1 may prevent such import from taking place.