Figure 2a:
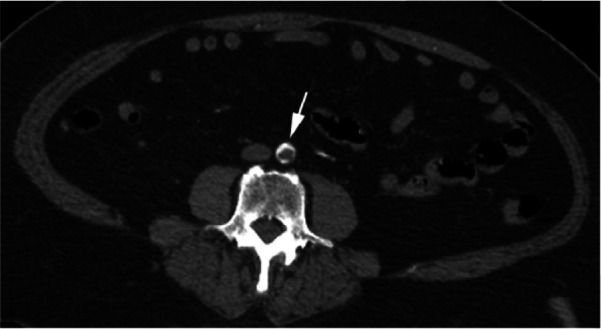
CTA images from a 63-year-old woman with COVID-19. Images through the (a) distal abdominal aorta, (b) proximal common iliac arteries, (c) external iliac arteries, (d) popliteal arteries, and (e) anterior tibial, posterior tibial, and peroneal arteries demonstrate lack of contrast opacification on the left (arrows). Hyperdensity along the periphery of the vessels in a and b corresponds to contrast rather than calcium. Note that the arrows in e point to the expected location of the vessels. (f) Oblique coronal reformatted CT image demonstrates clot at the aortic bifurcation (arrow).
