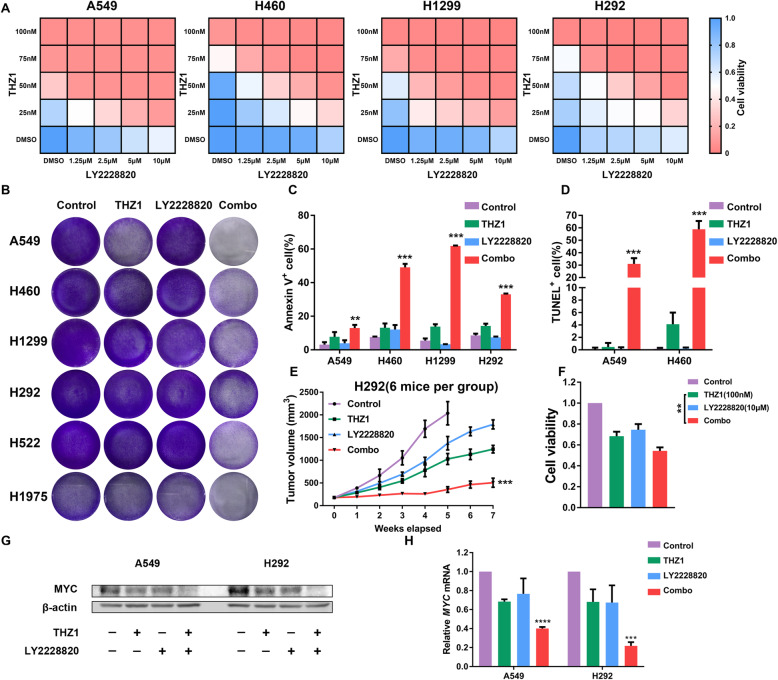
Fig. 4.
CDK7 inhibition sensitizes cancer cells to p38α inhibitor in NSCLC. a CCK8 viability assay following escalating concentrations of THZ1 and LY2228820 treatment for 48 h in NSCLC cells. b Representative images showing the response of NSCLC cell lines to the combination of THZ1 and LY2228820 treatment at 96 h. Cells were treated with THZ1 (50 nM), LY2228820 (5 μM), or the combination for 48 h and then cultured with fresh medium for another 48 h. In the end, cells were stained with crystal violet solution and photographed. c Quantification of the annexin V positive cell ratio after the combination of THZ1 (50 nM) and LY2228820 (5 μM) for 48 h (n = 3) (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 as compared to THZ1 group). d Quantification of the TUNEL positive cell ratio after the combination of THZ1 (50 nM) and LY2228820 (5 μM) for 48 h (n = 3) (***P < 0.001 as compared to THZ1 group). e Tumor growth curves of the H292 xenograft model treated with the combination of THZ1 and LY2228820 (n = 6) (***P < 0.001 as compared to THZ1 group). f CCK8 cell viability assay following THZ1 (100 nM) and LY2228820 (10 μM) treatment for 72 h in cancer cells from the PDX model (n = 4) (**P < 0.01). g Changes of MYC protein levels in A549 and H292 cells after the combination of THZ1 (50 nM) and LY2228820 (5 μM) for 48 h. β-actin was used as a loading control. h Relative changes of MYC mRNA levels in A549 and H292 cells after the combination of THZ1 (50 nM) and LY2228820 (5 μM) for 48 h. Results are normalized to β-actin (n = 3) (***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 as compared to control group)