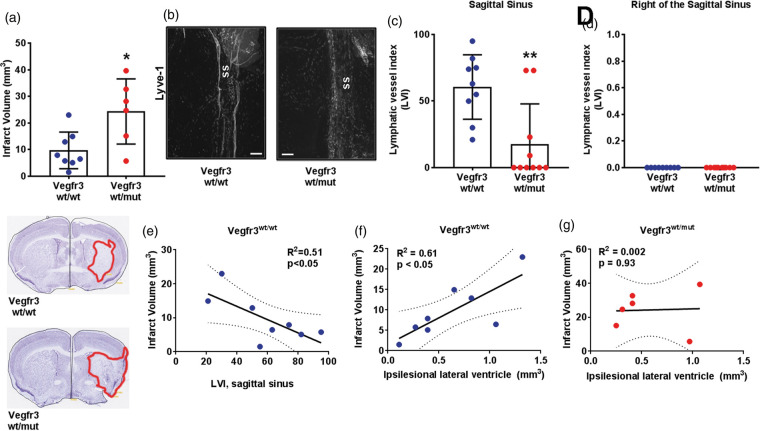
Figure 7.
Meningeal lymphatic hypoplasia increases infarct volumes after tMCAo. (a) Quantification of infarct volumes of Vegfr3wt/wt (blue circles) and Vegfr3wt/mut (red circles) mice two weeks following transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAo; n = 6–8 per group). Insets below graph show representative cresyl violet-stained cortical sections with infarcts highlighted in red. (b) Representative images of Lyve-1 + LVs at the sagittal sinus (ss). (c) Quantification of meningeal LVs at the sagittal sinus and (d) to the right of the sagittal sinus (p > 0.99) of Vegfr3wt/wt and Vegfr3wt/mut mice (n = 9–10 per group). (e) Sagittal sinus LVI correlates with decreased infarct volume in Vegfr3wt/wt mice. (f) Increased infarct volumes correlate with increased ipsilesional ventricle volumes in Vegfr3wt/wt (R2 = 0.61) but not in (g) Vegr3wt/mut (R2 = 0.002) mice. Meningeal LVI and infarct volumes were analyzed using a Mann–Whitney test and linear regression. All data presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Scale bar = 200 µm.