Figure 2.
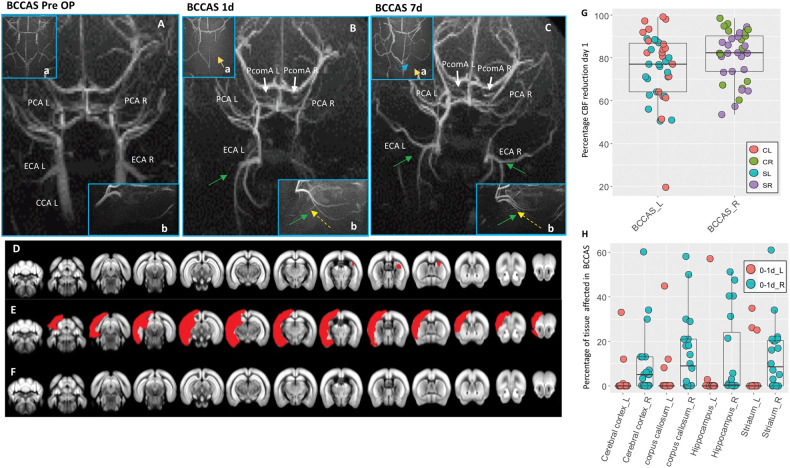
MRA and MRI phenotypes in BCCAS mice one to seven days post-surgery. (A–C) Vascular collateral plasticity during the first week post-surgery; (a), circle of Willis; (b), ECA flow. (A) Pre-surgery MRA, where PcomAs are not identifiable. (B) MRA one day post-surgery, showing recruitment of both PcomAs (white arrows), directing the blood flow to the PCAs, whose MRA intensity is increased, and left ECA retrograde flow (green arrow, yellow dashed line) and hypoperfused border zones between right ACA and right MCA (a, orange arrow). (C) MRA seven days post-surgery, characterized by increased PcomA (white arrows) and PCAs MRA intensity signal, recruitment of right ECA retrograde flow (green arrow, yellow dashed line), with a compensatory sustainment of the right anterior cerebral artery (ACA) territory (a, orange arrow) partially coming from the left hemisphere through the AcomA (blue dashed line). (D–F) Main ischemic lesion patterns observed in BCCAS 24 h post-surgery on T2-weighted MRI: small right subcortical lesions (D), big cortical and subcortical lesions (E) and no lesions detectable (F). (G) Percentage of CBF reduction at day 1 in BCCAS mice in left and right hemispheres, displaying more accentuated hypoperfusion in the right hemisphere, particularly in the frontal cortex. (H) Most affected brain regions in the BCCAS model 1 day post surgery are the watershed areas between right ACA and right MCA: right cerebral cortex, corpus callosum, striatum und hippocampus. CCA L: left common carotid artery; ECA L: left external carotid artery; ECA R: right external carotid artery; PCA L: left posterior cerebral artery; PCA R: right posterior cerebral artery; PcomA L: left posterior communicating artery; PcomA R: right posterior communicating artery. R: right; L: left. Pre-Op, pre-surgery.