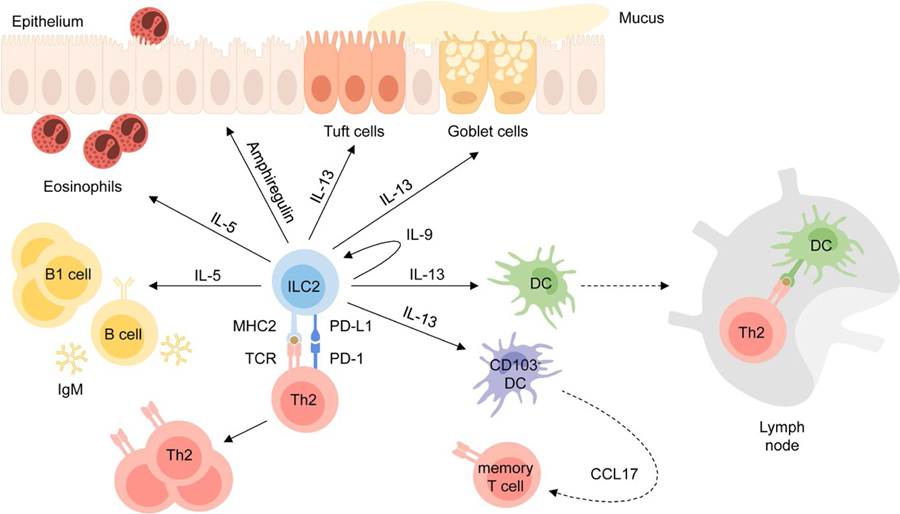
FIGURE 4.
ILC2 effector mechanisms. ILC2s have tissue-protective and pro-inflammatory effector functions. ILC2s produce IL-13 which promotes tuft cell and goblet cell hyperplasia, activates DCs to migrate to the lymph nodes, where they promote Th2 differentiation, and induces CCL17 production by CD103-DCs which recruits memory T cells to the site of inflammation. ILC2s also induce eosinophilia, B1 cell expansion and production of IgM by B cells via production of IL-5 and produce IL-9 which leads to autocrine activation. Interaction with Th2 cells via MHC2 and PD-L1 promotes Th2 differentiation and effector function. While these cytokines and surface molecules contribute to the development of tissue inflammation, the epidermal growth factor amphiregulin was shown to be important for tissue homeostasis and repair