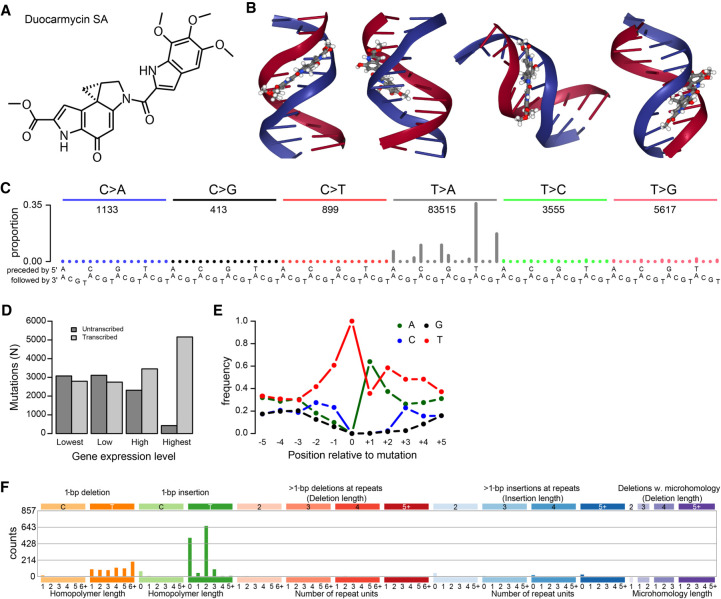
Figure 5.
Mutational signature of duocarmycin SA (duoSA). (A) duoSA, one of the naturally occurring duocarmycins. (B) Several views of the conformation of duoSA intercalated with DNA (source: PDB ID: 1DSM) (Smith et al. 2000; Rose et al. 2018). Duocarmycins slot into the minor groove of the DNA helix. (C) SBS mutation spectrum of one of the duoSA-treated HepG2 clones. (D) Transcriptional strand bias of T > A mutations induced by duoSA as a function of gene expression. (E) Extended sequence context specificity of T > A mutations induced by duoSA. (F) Indel spectrum of one of the duoSA-treated HepG2 clones.