Fig. 2.
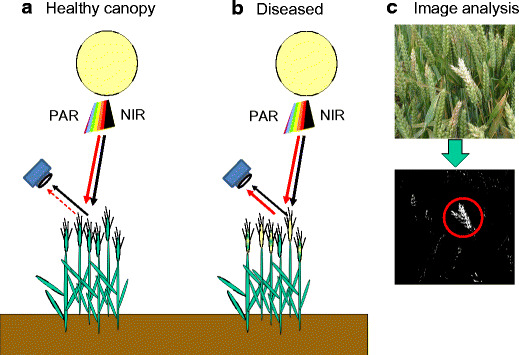
Illustration of a camera recording light reflected from a healthy or disease-affected canopy. The quality of light from the healthy canopy has a low ratio of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) to Near InfraRed (NIR), while this ratio is increased in the diseased canopy. Indices such as normal differential vegetation index (NDVI) can be used to improve classification of affected crops. A traditional camera needs to take duplicate images with different filters in front of the lens to allow this processing for classification of disease but modern hyperspectral or multispectral digital cameras can filter light reaching individual pixels of the image sensor surface, allowing images in different wavebands to be taken simultaneously, which can be processed using a computer. Such cameras can be smaller than a tennis ball enabling them to fit onto a drone (UAV). Alternatively, Fig. 2c shows processing of an image of Fusarium affected wheat from a standard digital camera into a simple black and white image, from which clusters of white pixels over a chosen threshold size can indicate an infected location
