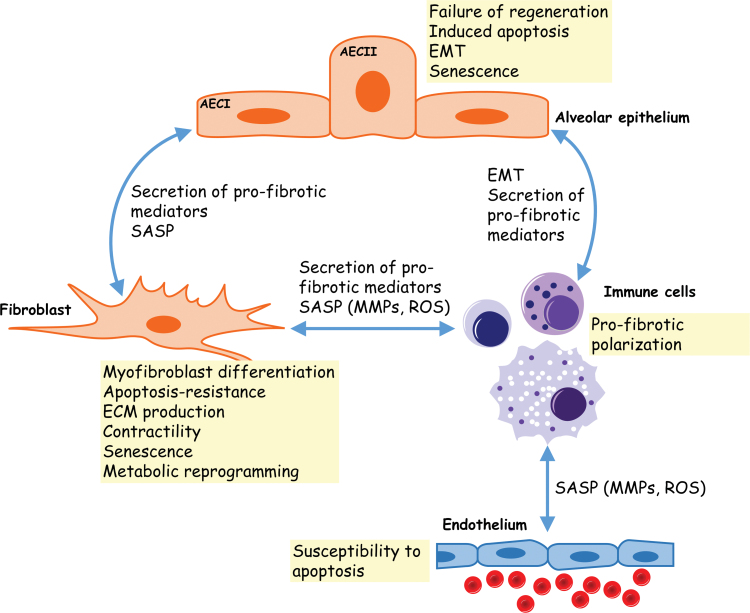
FIG. 1.
Cellular interactions in pulmonary fibrosis. Communication between the different cellular effectors of pulmonary fibrosis involves secreted/paracrine mediators. Injured alveolar epithelial cells secrete proinflammatory factors that may sustain the recruitment/activation of immune cells to the site of injury. Immune cells amplify the inflammatory response and may polarize to a more profibrotic response that promotes myofibroblast differentiation and ECM remodeling. The SASP of epithelial cells and myofibroblasts has also been proposed to alter the phenotype of neighboring cells. AECI, alveolar epithelial cell type I; AECII, alveolar epithelial cell type II; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SASP, senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Color images are available online.