Figure 6.
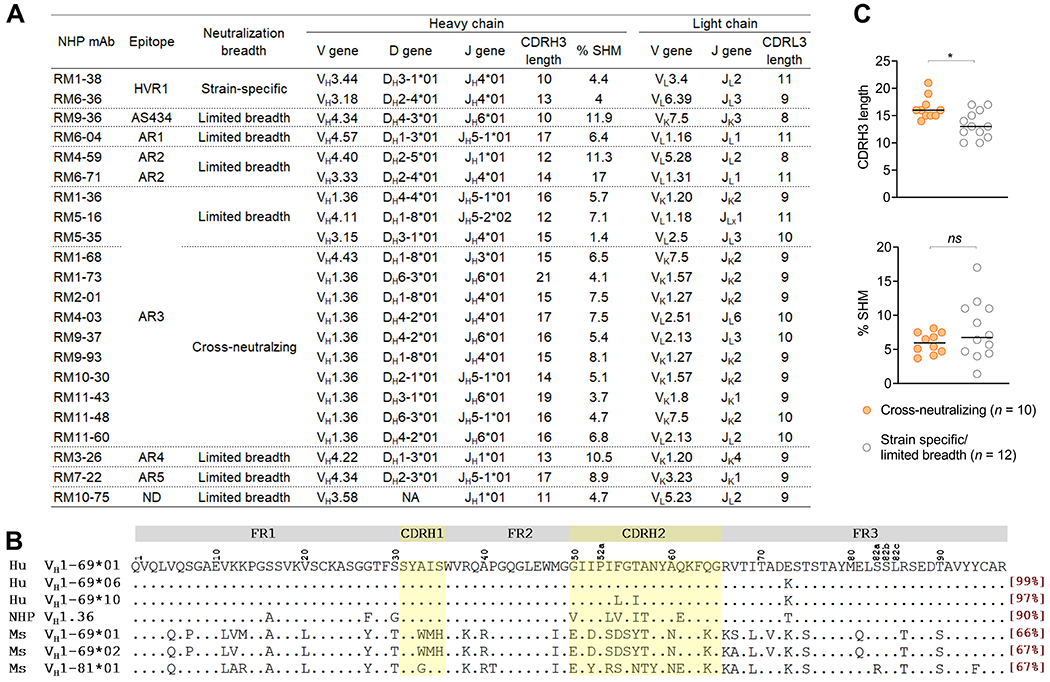
Summary of NHP neutralizing mAbs. (A) Specificity, function and genetic features of NHP neutralizing mAbs. Clonal lineages were assigned based on the following criteria: 1) matching of V and J gene usage, 2) identical CDR3 length, and 3) CDR3 nucleotide sequence homology >80%. CDR, complementarity-determining region. ND, not defined. NA, not available. CDR3 length is based on Kabat numbering, in which the CDRH3 is 2 amino acids shorter than in the IMGT definition. (B) Alignment of amino acid sequences of human VH1-69 gene and its homologues in NHPs and mice. Human VH1-69 sequences were exemplified by VH1-69*01 and *06, the most frequently used alleles by human HCV AR3-specific antibodies, and VH1-69*10, the closest human corresponding gene of to NHP VH1.36. The amino acid identity of each germline gene/allele compared to human VH1-69*01 allele is square-bracketed in red. FR, heavy chain framework. (C) Comparison of the CDRH3 length and SHM rate between cross-nAbs and strain-specific or limited breadth nAbs. P values were calculated by two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. *P < .05, ns, not significant.
