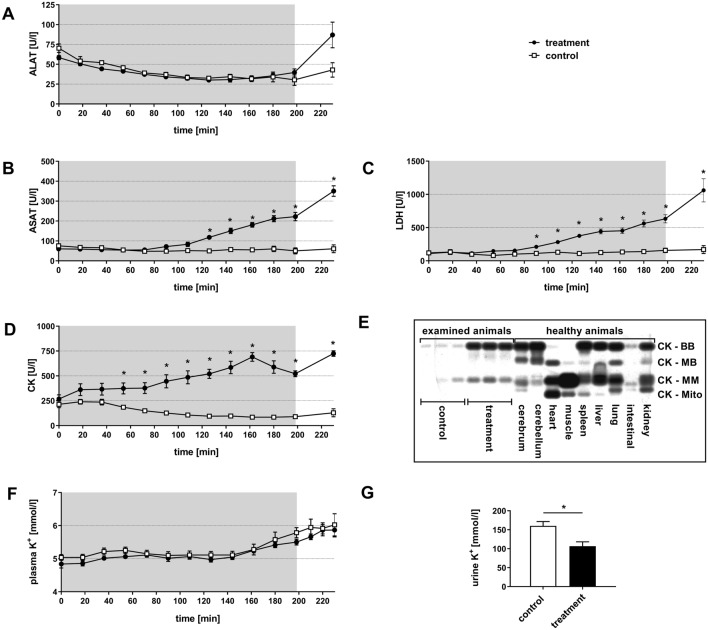
Figure 3.
Effect of normovolemic hemodilution on ALAT (A), ASAT (B), LDH (C), CK (D), CK isoenzymes (E) and K+ (F) in plasma in addition to K+ in urine (G). During hemodilution (grey background), animals were diluted using 5% HSA (control) or 12 vol% capsules (treatment) to a hematocrit of 5%. The plots (A-D, F, G) show the mean ± SEM of n = 8 animals per group. Asterisk indicates significance with p < 0.05 compared to the controls. CK-isoenzyme determination (E) in respectively three plasma samples per group of minute 162 (examined animals). Control animals showed slight bands of CK-BB and CK-MM, whereas the treatment group showed increased bands of CK-BB and CK-MM. Comparison of CK-isoenzyme pattern of the treatment group with the organ-specific pattern of organ homogenates of cerebrum, cerebellum, heart, muscle, spleen, liver, lung, intestinal and kidney of healthy untreated animals matched best with the spleen-specific pattern of CK-isoenzymes treatment bands with organ homogenates.