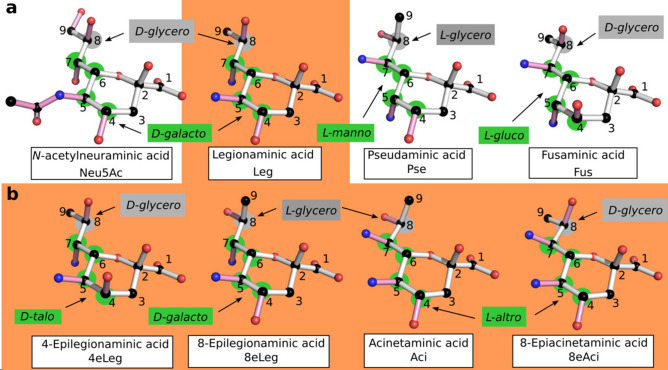
Figure 1.
Structure of known NulOs. The common, nine-carbon backbone of NulOs is represented with white bonds, and the carbons are numbered. The absolute configuration of each isomer is indicated in either gray or green depending on the concerned chiral centers, which are marked by disks of the corresponding color. (a) The three main NulOs families, according to their synthesis pathways, and the newly identified fusaminic acid (Fus). Neuraminic acid (Neu) is represented carrying an N-acetyl group in C5 (Neu5Ac), since it is the most commonly found species. Legionaminic (Leg), pseudaminic (Pse) and Fus carry N-linked groups in C5 and C7, which were omitted for clarity leaving only the nitrogen atom. (b) Isomers from the legionaminic acid synthesis pathway presenting different absolute configurations. As for Leg, N-linked groups carried at the C5 and C7 positions are represented by the nitrogen atom only. The orange background serves to highlight the common synthesis pathway of Leg isomers.
Figure taken from82.