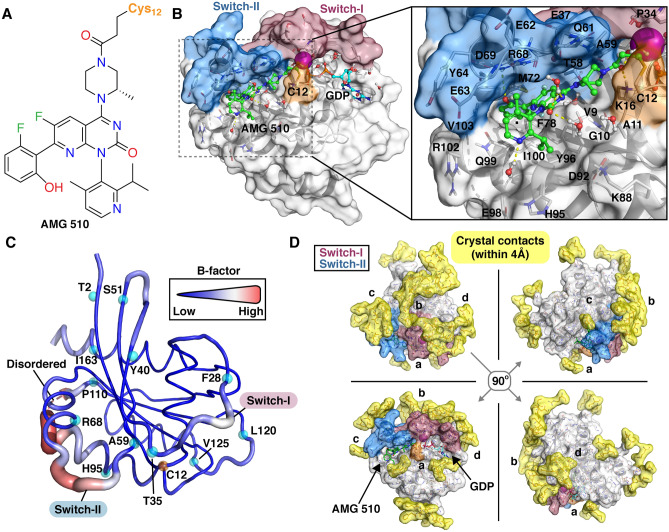
Figure 1.
KRAS(G12C)–AMG 510 structure. (A) Chemical structure of AMG 510. (B) Crystal structure of KRAS(G12C)–AMG 510 complex (PDB ID: 6oim). AMG 510 (green) binds to the SII-P and exploits a cryptic pocket formed by H95/Y96/Q99. (C) B-factor values of KRAS(G12C)–AMG 510 structure. Thick and red ribbon indicate a high B-factor value, whereas thin and blue a low value. Cα-atoms of start and end residues of higher B-factor regions are highlighted with cyan spheres (regions: G0–T2; F28–T35; Y40–S51; A59–R68; H95–P110; L120–V125; I163–H166). A disordered region of the structure, D105–E107, is indicated with dashed red line. (D) Observed crystal contacts in KRAS(G12C)–AMG 510 structure. Residues within 4 Å of the protein are shown in sticks together with their molecular surface (yellow). In (B, D) KRAS switch regions: switch-I: residues 25–40 and switch-II: residues 58–72 are highlighted with red and blue, respectively. C12 is highlighted with orange.