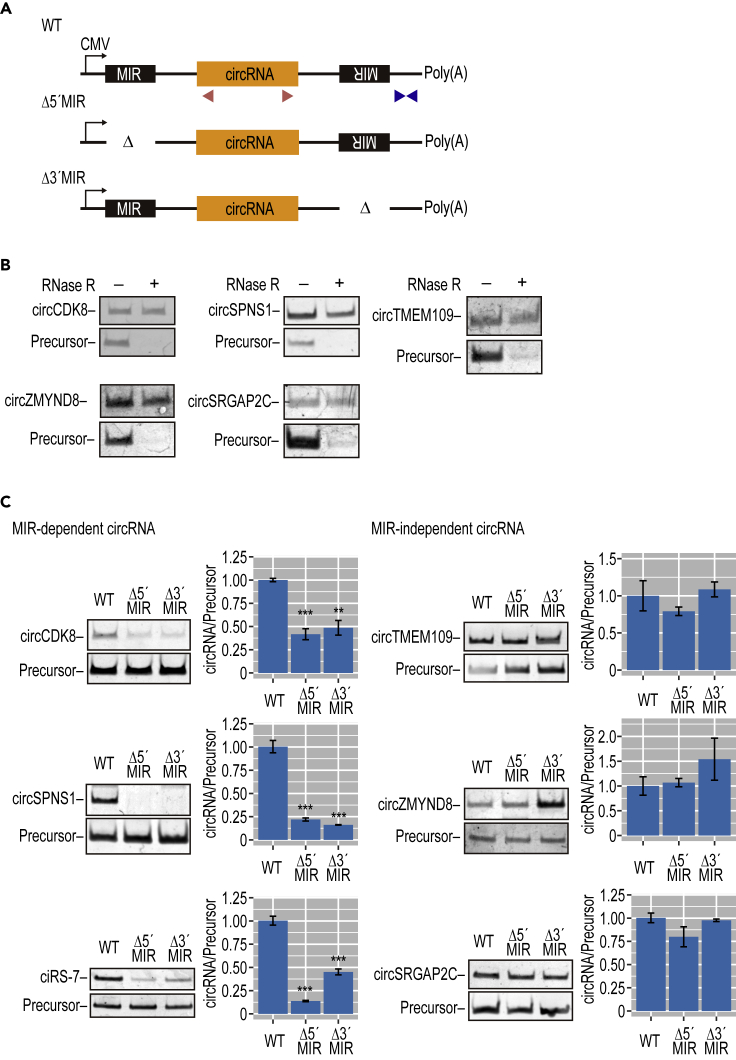
Figure 3.
Several Other Human MIR-Dependent circRNAs Were Identified
(A) Schematic structure of plasmid expressing wild-type (WT) or MIR deletions (Δ5′MIR, Δ3′MIR), which was constructed for five circRNAs. Red and blue triangles indicate the positions of PCR primers to detect circRNA and precursors, respectively.
(B) RT-PCR detection of five circRNAs in mouse N2A cells transfected with the plasmids depicted in (A). Total RNA from the cells was treated with (+) or without (−) RNase R to discriminate the circular from the linear structure.
(C) Identification of MIR-dependent and MIR-independent circRNAs. RT-PCR analysis of circRNAs and their precursors, expressed from the plasmid types depicted in (A). Total RNA was also quantified by RT-qPCR. The circRNA expression levels were normalized to the expression levels of precursor RNA as controls (circRNA/Precursor). Values are relative to the value of control wild-type clones (WT). Means ± SD are given for three independent experiments (∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01).