Figure 4.
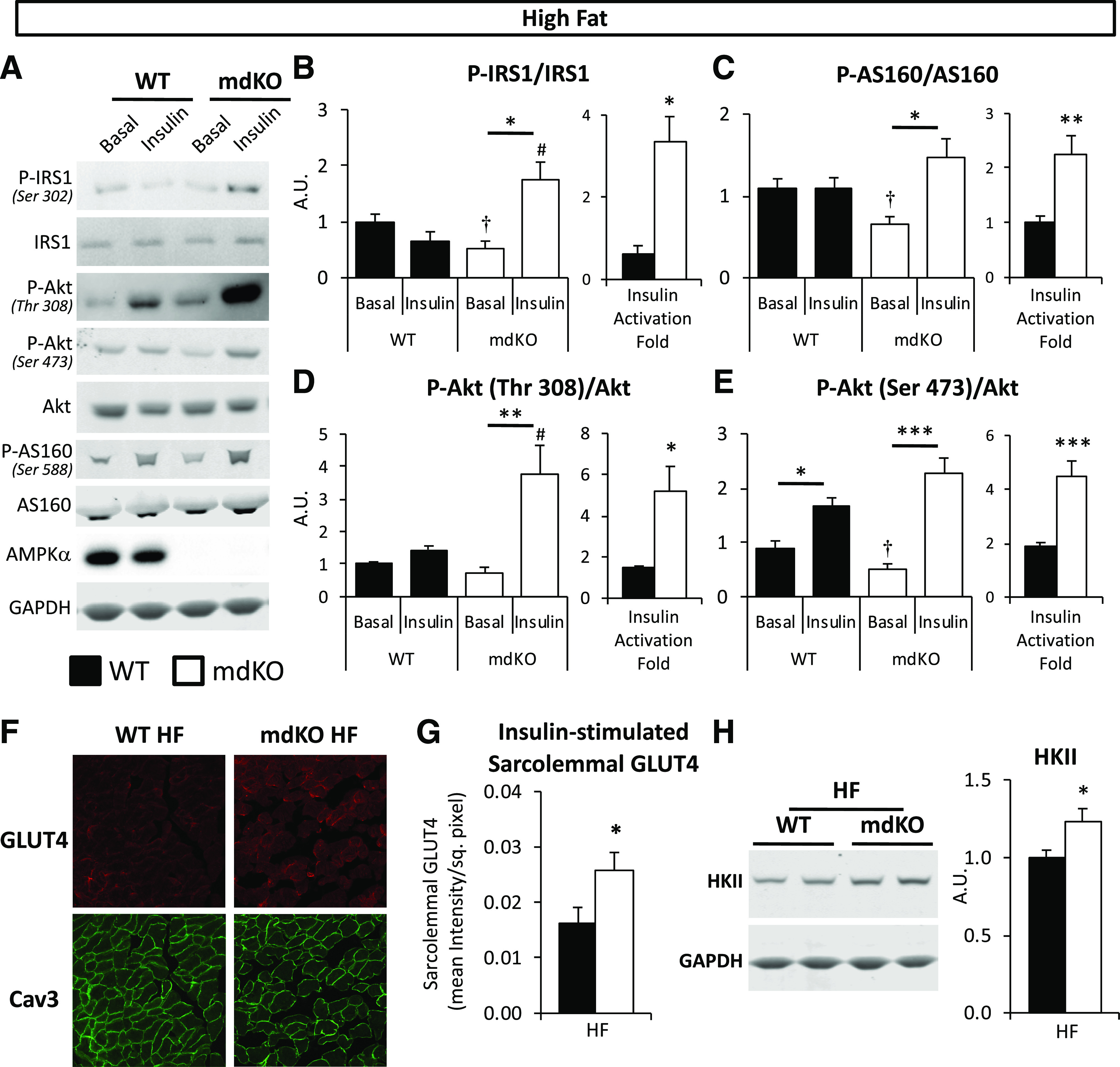
Insulin signaling and GLUT4 translocation are increased in muscle of HF-fed mdKO mice. A: Vastus lateralis homogenates from 5-h–fasted (basal) or insulin-clamped mice were applied to a 4–12% SDS-PAGE. Western blotting was performed for P-IRS1 (Ser302), IRS1, P-Akt (Thr308 and Ser473), Akt, P-AS160 (Ser588), AS160, AMPKα, and GAPDH. B–E: Integrated intensities were normalized to respective total protein. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. basal (same genotype), #P < 0.05 vs. WT (same condition) by Tukey post hoc; †P < 0.05 mdKO basal vs. WT basal by Student t test. N = 8/group. Insulin-induced activation fold for IRS1, AS160, and Akt in insulin-clamped HF WT and mdKO vastus lateralis, relative to the 5-h–fasted basal state, was calculated as follows: (phospho/total ratio)insulin-stimulated state/(phospho/total ratio)fasted state. F and G: Confocal imaging of GLUT4 and plasma membrane marker Caveolin-3 (Cav3) was performed on clamped (insulin-stimulated) gastrocnemius cryosections. Quantification of sarcolemmal GLUT4 was performed by ImageJ. N = 11–15/group. H: Vastus lateralis homogenates were applied to a 4–12% SDS-PAGE. Western blotting was performed for HKII and GAPDH. Integrated intensities were normalized to GAPDH. Integrities were normalized to WT HF intensities. N = 8/group. A.U., arbitrary units; sq., square.
